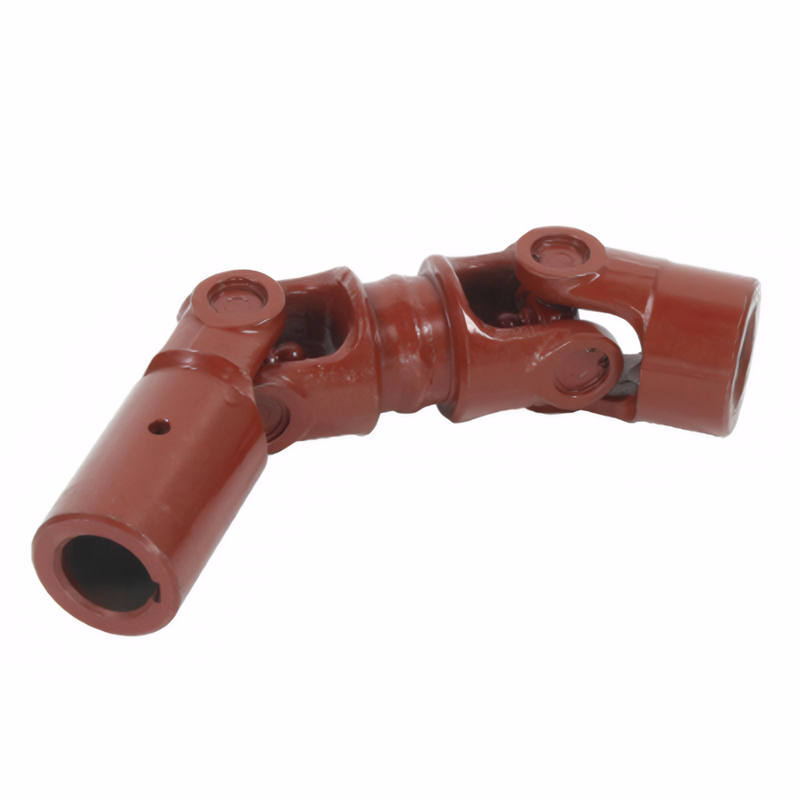
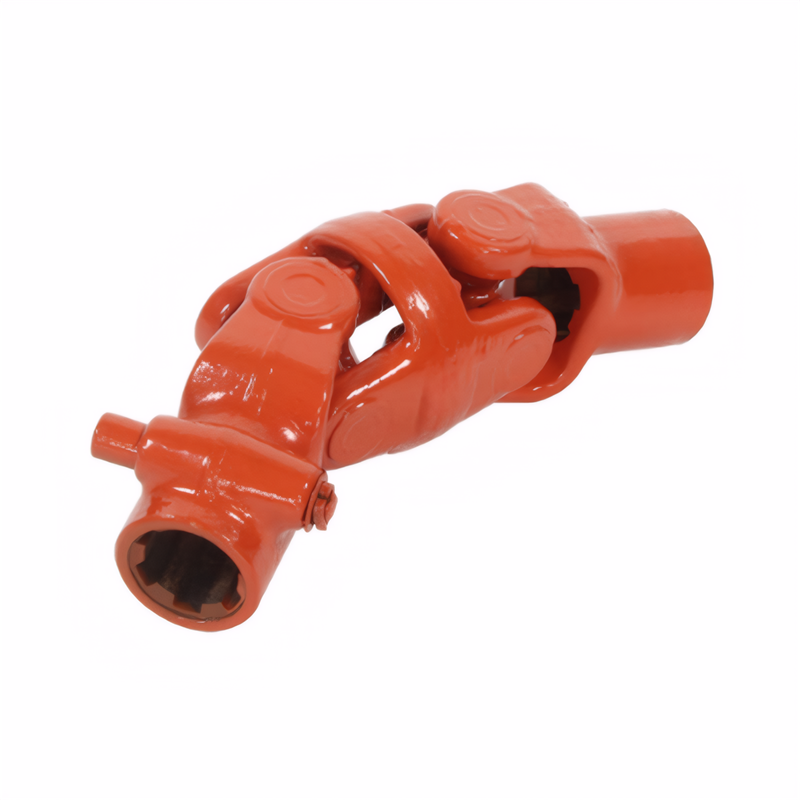
Preventive measures for drive shaft breakage
Preventing Drive Shaft Failure: Proactive Measures to Avoid Breakage
The drive shaft is a vital component that transfers torque from the transmission to the wheels, enabling smooth acceleration and reliable power delivery. However, factors like excessive stress, poor maintenance, or manufacturing flaws can lead to catastrophic failure. A broken drive shaft can immobilize your vehicle, damage surrounding parts, and compromise safety. By implementing preventive strategies, you can extend the lifespan of your drive shaft and reduce the risk of sudden failure.
Regular Inspections for Early Detection of Wear
One of the most effective ways to prevent drive shaft failure is through routine visual and physical inspections. Start by examining the shaft for visible signs of damage, such as cracks, dents, or corrosion. Pay close attention to high-stress areas like the flanges, welds, and center support bearing (if applicable). Corrosion or rust can weaken the metal over time, making it more susceptible to fractures. Next, check for excessive play by gently moving the shaft side-to-side or up-and-down. While minor movement is normal, significant looseness suggests worn universal joints (U-joints) or CV joints, which can destabilize the shaft. Additionally, listen for unusual noises during operation, such as clunking, grinding, or squeaking, which may indicate internal joint wear or misalignment. Addressing these issues early can prevent minor problems from escalating into a full breakage.
Proper Torque Specifications and Fastener Maintenance
Drive shaft failure often stems from improperly secured components, such as loose bolts or nuts. These fasteners hold the shaft in place and ensure alignment with the transmission and differential. Over time, vibrations and thermal expansion can cause bolts to loosen, leading to misalignment and uneven stress distribution. To prevent this, always follow the manufacturer’s recommended torque specifications when installing or reinstalling the drive shaft. Use a calibrated torque wrench to tighten bolts to the correct value, and consider applying thread-locking compound to prevent loosening under vibration. During routine maintenance, such as oil changes or tire rotations, recheck the torque of these fasteners to ensure they remain secure. Additionally, inspect the condition of the bolts and nuts for signs of stretching, corrosion, or damage, replacing them if necessary to maintain a reliable connection.
Avoiding Overloading and Excessive Stress
Drive shafts are designed to handle specific torque loads and operating conditions. Subjecting them to excessive stress, such as towing loads beyond their capacity or aggressive driving on rough terrain, can accelerate wear and increase the risk of failure. For example, overloading a vehicle can cause the drive shaft to bend or twist under pressure, leading to fatigue cracks over time. Similarly, sudden acceleration or hard braking can create shock loads that strain the shaft and its joints. To mitigate these risks, adhere to your vehicle’s towing and payload limits, and avoid rapid throttle inputs or abrupt gear changes. If you frequently drive on uneven surfaces or off-road, consider upgrading to a heavy-duty drive shaft (if compatible with your vehicle) to better withstand the demands of such conditions.
Ensuring Proper Alignment and Balancing
Misalignment or imbalance in the drive shaft can create uneven stress distribution, leading to premature wear or fractures. This often occurs after component replacements, such as a new transmission or differential, or after suspension modifications. To prevent alignment issues, have the drive shaft inspected and adjusted by a qualified mechanic whenever major drivetrain or suspension work is performed. Balancing is equally critical; an unbalanced drive shaft will wobble at high speeds, causing vibrations that stress the shaft and its supporting components. If you notice persistent vibrations, especially at specific RPM ranges, have the shaft professionally balanced to eliminate imbalances. Regular alignment and balancing checks help maintain smooth operation and reduce the likelihood of fatigue-related failures.
A broken drive shaft can disrupt your journey and lead to costly repairs, but many failures are preventable with proactive care. By conducting regular inspections, maintaining proper torque specifications, avoiding overloading, and ensuring alignment and balance, you can protect this essential component from premature wear. Prioritizing these measures not only enhances vehicle reliability but also promotes safer driving conditions for you and others on the road.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
