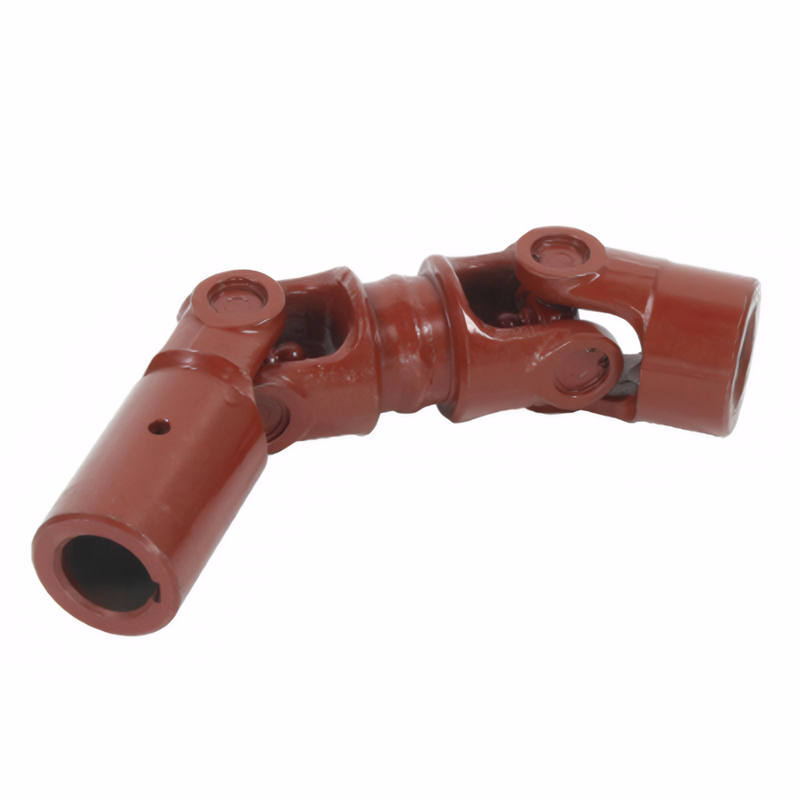
Testing methods for drive shafts after maintenance
Post-Maintenance Drive Shaft Testing: Ensuring Optimal Performance and Safety
After performing maintenance on a vehicle’s drive shaft—such as replacing universal joints, lubricating components, or correcting alignment—a systematic testing process is essential to verify functionality and prevent drivetrain issues. Testing helps identify residual vibrations, noise, or mechanical faults that could indicate incomplete repairs or overlooked problems. Below are key steps to evaluate drive shaft performance following maintenance work, ensuring reliability under real-world driving conditions.
Conducting a Static Visual Inspection Before Engine Startup
Before starting the vehicle, perform a thorough visual check of the drive shaft and surrounding components to confirm all maintenance tasks were completed correctly. Verify that all bolts, nuts, and fasteners are tightened to the manufacturer’s specified torque values, as loose hardware can cause vibrations or component separation during operation. Inspect newly installed parts, such as U-joints or center support bearings, for proper seating and alignment with adjacent drivetrain components.
Check for signs of grease leakage around lubricated joints, which may indicate over-lubrication or damaged seals. Ensure protective boots on CV joints (if applicable) are securely fastened and free of tears, as exposed joints are vulnerable to contamination. Additionally, examine the drive shaft for any tools or debris left behind during repairs, as foreign objects can cause damage when the shaft rotates. Addressing these issues before engine startup prevents secondary failures and ensures a safer testing environment.
Road Testing: Monitoring for Vibrations, Noise, and Handling Anomalies
The most critical phase of post-maintenance testing involves driving the vehicle under controlled conditions to assess drive shaft performance. Begin with a short, low-speed test on a smooth, level surface to check for unusual noises, such as clunking, grinding, or squeaking, which may indicate improperly installed U-joints or misaligned components. Gradually increase speed to monitor for vibrations, which often manifest as steering wheel shaking or seat oscillations, signaling imbalances or bent shafts.
During acceleration and deceleration, listen for rhythmic thumping or binding sounds, which could stem from worn bearings or insufficient lubrication. Test the vehicle’s handling by making gentle turns to evaluate CV joint function (if equipped), as damaged joints may produce clicking noises or resistance during steering inputs. If possible, replicate the driving conditions that initially prompted maintenance—such as uneven terrain or high-torque scenarios—to ensure the repairs hold under stress. Document any abnormalities for further diagnosis.
Elevated Vehicle Inspection: Verifying Component Movement and Fastener Security
After road testing, perform a secondary inspection with the vehicle safely elevated on jack stands to assess drive shaft behavior under load without engine interference. Rotate the drive shaft manually (if accessible) to check for smooth, consistent motion. Resistance or grinding sensations may indicate seized U-joints or misaligned yokes, while excessive play suggests worn bearings or loose fasteners.
Inspect mounting brackets and center support bearings for signs of stress, such as cracks or deformation, which can occur if the shaft was improperly balanced or aligned during installation. Verify that all drive shaft angles match the manufacturer’s specifications, as incorrect angles accelerate U-joint wear and cause vibrations. Finally, re-tighten all bolts and nuts to account for thermal expansion or settling during initial operation. This step ensures long-term reliability and prevents loosening over time.
Post-maintenance drive shaft testing combines static checks, dynamic road evaluations, and elevated inspections to confirm repairs were successful. Visual inspections before engine startup catch overlooked issues like loose fasteners or grease leaks, while road tests reveal vibrations or noise linked to improper installation. Elevated vehicle checks allow for hands-on assessment of component movement and alignment, ensuring the drive shaft operates smoothly under load. By following these steps, drivers and mechanics can validate maintenance work, prevent premature failures, and maintain drivetrain integrity across diverse driving conditions.
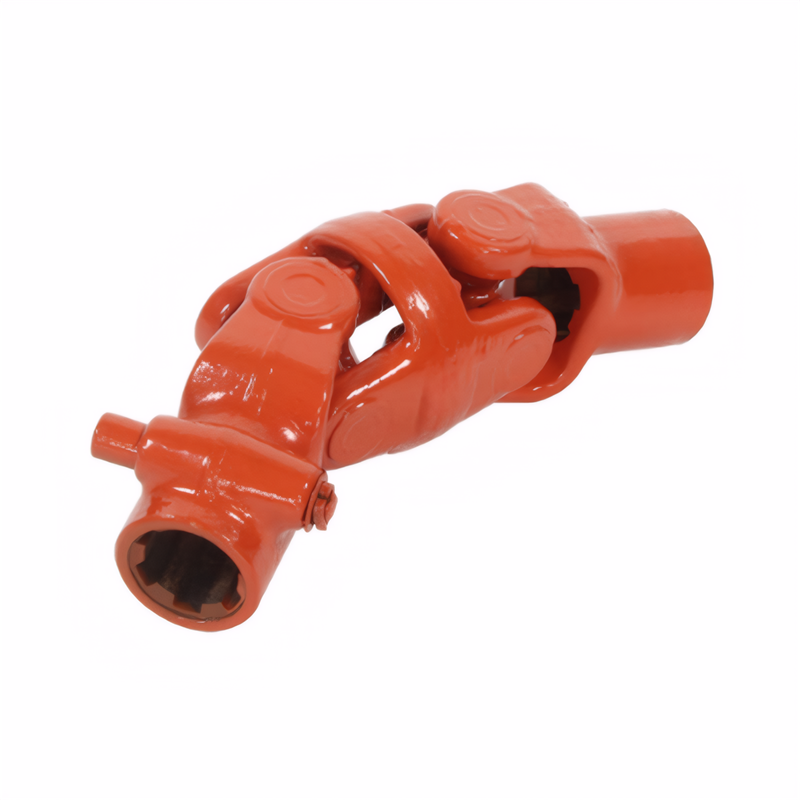
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
