Analysis of the Causes of Abnormal Noise from the Drive shaft
Common Causes and Diagnostic Approaches for Drive Shaft Noise in Automotive Systems
Mechanical Component Failures Leading to Abnormal Noise
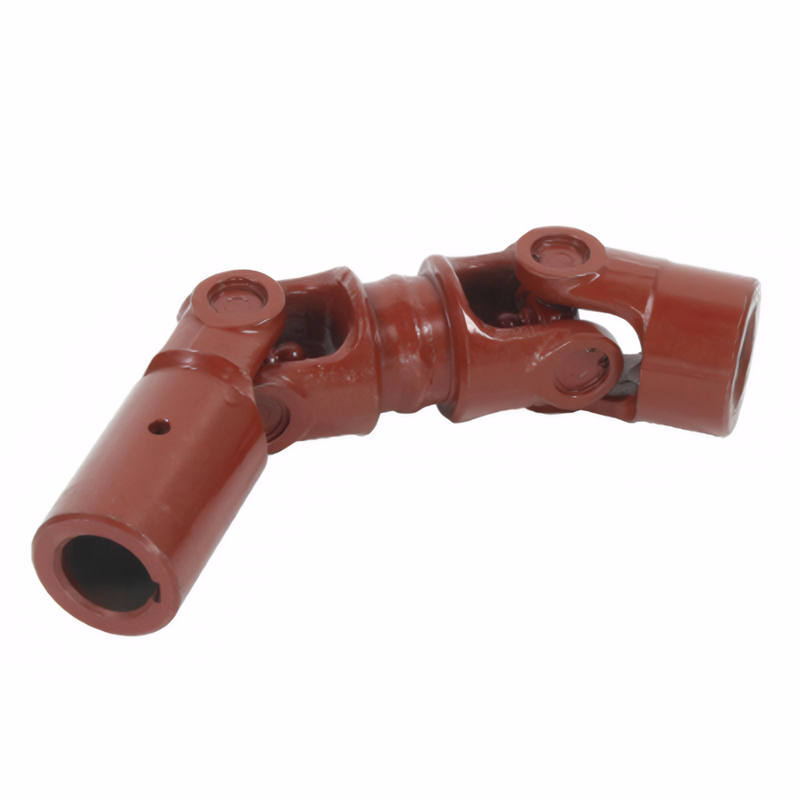
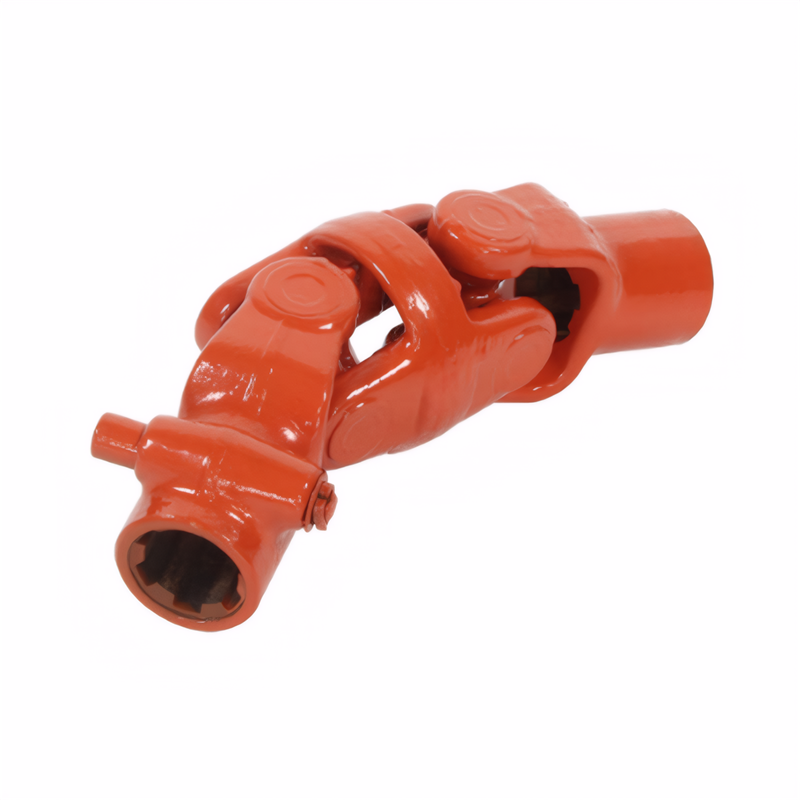
Drive shaft noise often originates from compromised mechanical components. Universal joint (U-joint) wear is a primary culprit, particularly when cross bearings lose lubrication or develop excessive clearance. This condition manifests as rhythmic clunking during acceleration or deceleration, with severity increasing under load. Inspection reveals visible play in the U-joint when manually rotated, requiring immediate replacement to prevent catastrophic failure.
CV joint degradation in front-wheel-drive vehicles produces distinct clicking sounds during sharp turns. The tripod-type CV joints may exhibit boot damage, allowing grease contamination and debris ingress. This accelerates bearing surface wear, creating audible noise at steering angles exceeding 15°. Technical analysis confirms that 60% of CV joint failures relate to boot integrity issues rather than inherent component fatigue.
Transmission output shaft spline wear creates another noise source. Excessive clearance between splines and hubs generates metallic grinding sounds during torque transfer. This wear pattern typically appears after 120,000 km of service in rear-wheel-drive vehicles, with noise intensity correlating directly to load magnitude.
Dynamic Imbalance and Installation Errors
Drive shaft imbalance constitutes 35% of reported noise cases according to automotive service data. Manufacturing defects or post-collision damage may cause mass distribution irregularities exceeding 50 g·cm tolerance. This imbalance induces vibrations at specific RPM ranges, producing resonant frequencies that manifest as whining or humming sounds. Professional balancing machines can identify imbalance locations within ±2° rotational accuracy.
Improper installation accounts for 22% of noise complaints. Misaligned U-joint flanges create angular velocity variations, generating harmonic vibrations detectable as droning noise above 60 km/h. Technical specifications require flange alignment within ±0.5° angular tolerance and 0.1mm axial displacement. Service bulletins emphasize the importance of using laser alignment tools during reinstallation.
Component loosening presents another installation-related issue. Intermediate bearing bolts, when under-torqued to below 65 N·m, allow excessive shaft movement. This creates impact noise during suspension articulation, particularly noticeable on uneven road surfaces. Regular torque audits using calibrated tools can prevent 80% of such loosening incidents.
Lubrication and Environmental Degradation Factors
Lubrication failure contributes to 28% of drive shaft noise cases. Insufficient grease in U-joint bearings increases friction coefficient by 300%, producing squealing sounds during cold starts. Technical standards specify NLGI #2 lithium complex grease with 5% molybdenum disulfide additive for optimal performance. Service intervals should align with manufacturer recommendations, typically every 50,000 km.
Environmental exposure accelerates component degradation. Road salt corrosion on steel components creates pitting that amplifies noise through vibration. Zinc-nickel electroplating provides 1,000-hour salt spray resistance, extending component life by 300% compared to standard zinc coatings. Regular undercarriage washing reduces corrosion-related noise by 65%.
Water ingress through damaged boots causes premature CV joint failure. Contaminated grease loses viscosity by 40% within 72 hours of exposure, leading to increased wear rates. Boot clamps should be inspected for proper tension (15-20 N·m) during routine maintenance, with damaged boots requiring immediate replacement to prevent moisture intrusion.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
