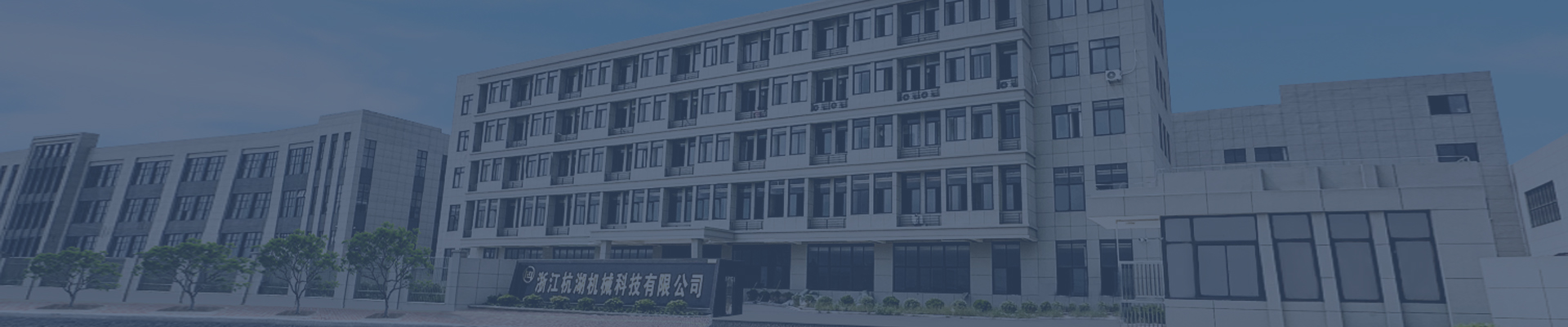
The hazard of a broken dust cover for the drive shaft
The Hidden Dangers of a Cracked Drive Shaft Boot: Protecting Your Vehicle’s Drivetrain
A drive shaft boot, often referred to as a bellows or protective cover, plays a critical role in safeguarding the joints and components of your vehicle’s drivetrain. Typically made of rubber or thermoplastic, these boots seal out dirt, moisture, and debris while retaining lubrication around universal joints (U-joints) or constant-velocity (CV) joints. When a boot cracks or tears, it exposes sensitive parts to contamination, leading to accelerated wear and potential failure. Understanding the risks associated with a damaged drive shaft boot can help drivers prioritize timely repairs and avoid costly drivetrain damage.
Contamination of Joint Components
The primary function of a drive shaft boot is to create a barrier between the joint’s internal components and external contaminants. A cracked boot allows road grime, sand, salt, and water to infiltrate the joint, where they mix with existing grease to form abrasive sludge. This mixture erodes the smooth surfaces of bearings, needle rollers, and trunnions in U-joints or the spherical elements in CV joints. Over time, this contamination causes pitting, scoring, and excessive friction, which generates heat and accelerates component degradation. For example, a U-joint exposed to contaminated grease may develop play or stiffness, leading to vibrations or clunking noises during acceleration or deceleration. Similarly, a compromised CV joint boot can cause the joint to seize or fail catastrophically, especially in front-wheel-drive or all-wheel-drive vehicles where these joints handle significant torque and steering forces.
Loss of Lubrication and Increased Friction
Drive shaft boots also retain specialized grease designed to reduce friction and dissipate heat within the joint. When a boot cracks, this lubricant escapes, leaving the joint’s moving parts to operate dry or with insufficient lubrication. Without proper grease, metal-to-metal contact increases, creating intense friction that wears down components rapidly. In U-joints, this can manifest as a binding sensation during turns or uneven power distribution to the wheels. CV joints may produce clicking or popping sounds when turning, indicating insufficient lubrication and impending failure. The lack of lubrication also raises operating temperatures, which can warp or deform joint components, further compromising drivetrain stability. Prolonged exposure to dry conditions may even cause the joint to lock up, resulting in a sudden loss of power to the wheels and potential loss of vehicle control.
Risk of Complete Joint Failure and Drivetrain Damage
If left unaddressed, a cracked drive shaft boot often leads to complete joint failure, which can have cascading effects on the entire drivetrain. A severely worn U-joint may snap under stress, causing the drive shaft to detach from the transmission or differential. This sudden disconnection can damage surrounding components, such as exhaust systems, brake lines, or suspension parts, and leave the vehicle immobile. In CV joints, a torn boot followed by joint failure can disrupt power transfer to the wheels, leading to uneven acceleration or a complete inability to move. Repairing drivetrain damage caused by a failed joint is often more expensive and time-consuming than replacing a cracked boot early. Additionally, driving with a damaged boot may void warranty coverage or insurance claims if the issue is deemed to result from negligence.
Impact on Vehicle Safety and Handling
A compromised drive shaft boot indirectly affects vehicle safety by altering handling and responsiveness. As joints wear due to contamination or lubrication loss, the drivetrain may transmit vibrations or noises through the chassis, making it harder for the driver to detect other potential issues. In extreme cases, a failing joint can cause sudden shifts in power delivery, such as during high-speed cornering or hard acceleration, increasing the risk of skidding or loss of traction. For example, a rear-wheel-drive vehicle with a damaged U-joint boot might exhibit unpredictable throttle response, while a front-wheel-drive car with a failing CV joint could struggle to maintain steering precision. These handling inconsistencies demand heightened driver attention and reduce overall confidence in the vehicle’s reliability.
A cracked drive shaft boot is not a minor inconvenience—it’s a warning sign of impending drivetrain trouble. By allowing contaminants to infiltrate, lubrication to escape, and joints to degrade, a damaged boot sets the stage for costly repairs and safety hazards. Regular inspections during routine maintenance, such as oil changes or tire rotations, can help identify boot cracks early. Addressing these issues promptly by cleaning the joint, replacing the boot, and replenishing grease preserves drivetrain integrity and ensures smooth, reliable performance. Neglecting a cracked boot risks stranding you on the road or facing extensive repairs, emphasizing the importance of proactive drivetrain care.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
