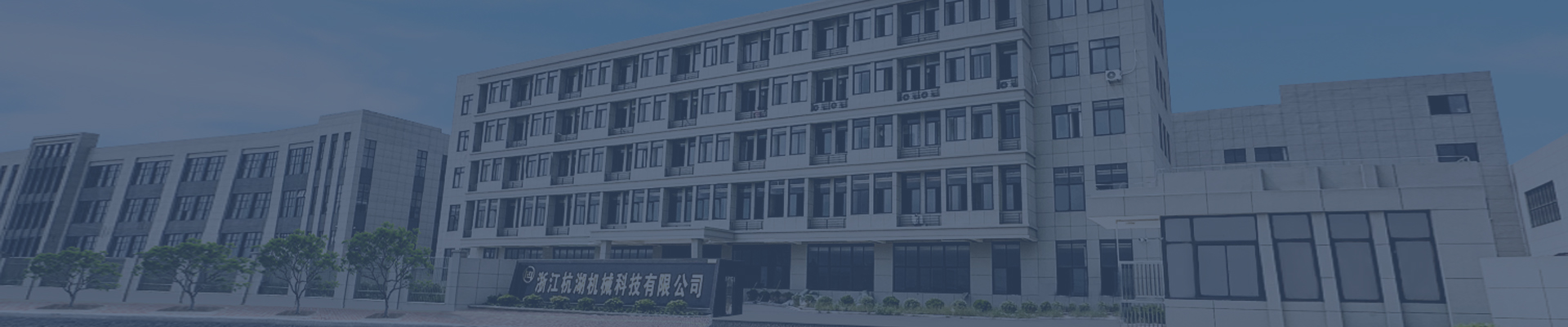
The manifestation of abnormal noise from the drive shaft when turning
Understanding Drive Shaft Noises During Turns: Symptoms and Diagnostic Clues
Drive shafts play a critical role in transferring power from the transmission to the wheels while accommodating changes in drivetrain angles during steering maneuvers. When abnormal noises occur specifically during turns, it often signals underlying issues with components like universal joints (U-joints), CV joints, or alignment. Identifying the nature and context of these sounds helps pinpoint the root cause, enabling targeted repairs before further damage occurs. Below is a detailed breakdown of how drive shaft-related noises manifest during turns and what they indicate.
Clicking or Popping Sounds During Sharp Turns
One of the most common drive shaft-related noises during turns is a rhythmic clicking or popping sound, often heard when steering sharply at low speeds, such as in parking lots or tight corners. This noise typically originates from worn or damaged CV joints, which are designed to maintain constant velocity even as the drive shaft angles change. CV joints rely on a series of ball bearings encased in a protective boot filled with grease. Over time, the boot may crack or tear, allowing grease to leak out and contaminants like dirt or moisture to enter. This leads to accelerated wear of the bearings, causing them to click or pop as they move within the joint housing during angular movement.
The clicking sound becomes more pronounced during turns because the CV joint is under greater stress, flexing to accommodate the steering angle. If the noise is isolated to one side of the vehicle, it often indicates a problem with the outboard CV joint (connected to the wheel hub), as this joint experiences the most extreme angles during turns. In contrast, a clicking noise from both sides may suggest issues with the inboard joints or a misaligned drivetrain. Ignoring these sounds can lead to complete joint failure, resulting in loss of power to the wheels or catastrophic drivetrain damage.
Clunking or Banging Noises When Changing Direction
A clunking or banging noise during turns, especially when transitioning from forward to reverse or vice versa, often points to loose or worn U-joints. U-joints connect the drive shaft to the transmission and differential, allowing flexibility as the suspension moves and the vehicle steers. These joints consist of needle bearings held in place by a cross-shaped yoke, which must rotate smoothly to prevent vibrations or noise. If the U-joint bearings become worn or the retaining clips loosen, the joint develops excessive play, causing it to clunk or bang as it shifts position during directional changes.
This noise is most noticeable during slow-speed turns because the drivetrain experiences rapid torque reversals, exacerbating the movement of a loose U-joint. In severe cases, the clunking may be accompanied by vibrations felt through the steering wheel or floorboard, indicating significant wear or impending failure. Additionally, a damaged or bent drive shaft can produce similar noises, as it may strike surrounding components during angular movement. Inspecting U-joints for rust, grease leakage, or visible play by hand (with the vehicle safely lifted) helps confirm their condition.
Grinding or Groaning Noises at Steady Turning Speeds
A persistent grinding or groaning noise during steady turns, such as when navigating a roundabout or long curve, often suggests a lack of lubrication or severe wear in drive shaft components. This type of noise is commonly associated with CV joints that have lost all grease due to a ruptured boot, leaving the bearings to grind against each other without lubrication. The friction generates heat and metal-on-metal contact, producing a distinctive groaning sound that worsens as the joint deteriorates further.
Similarly, a grinding noise may indicate a misaligned drive shaft or damaged center support bearing in two-piece drive shaft systems. Misalignment causes the shaft to operate at an abnormal angle, increasing friction between the shaft and its supporting components. The center support bearing, which holds the drive shaft in place, may also wear out over time, allowing the shaft to sag or vibrate excessively during turns. This vibration can create a grinding noise as the shaft contacts nearby parts or experiences internal stress. Checking for proper alignment and inspecting the center support bearing for wear or damage is essential to resolve this issue.
Drive shaft-related noises during turns are often symptoms of worn or damaged components like CV joints, U-joints, or alignment issues. Clicking or popping sounds suggest CV joint problems, while clunking noises point to loose U-joints. Grinding or groaning sounds indicate severe wear or lubrication failure. Addressing these noises promptly through visual inspection, lubrication checks, and component replacement prevents further damage and ensures safe drivetrain operation. Regular maintenance, including boot inspections and alignment verifications, helps minimize the risk of turn-related drive shaft issues.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
