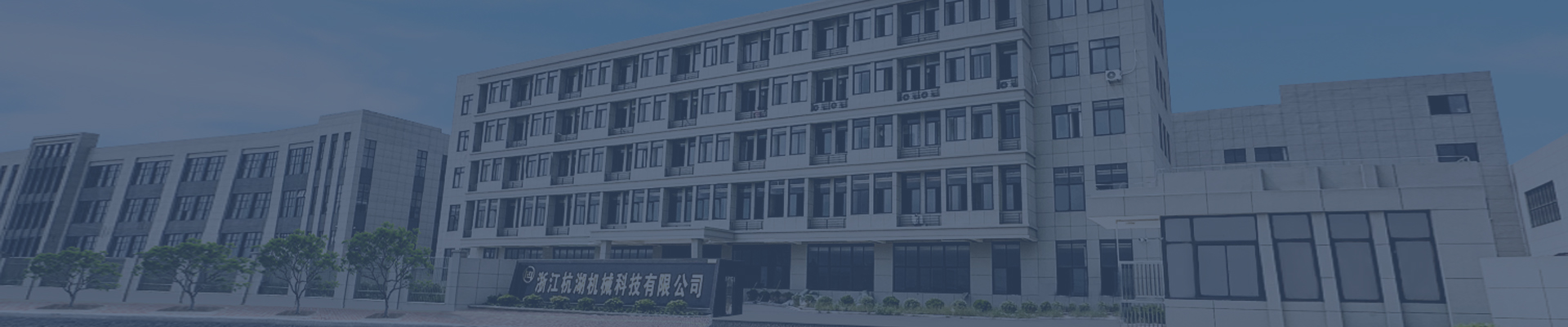
The characteristics of abnormal noise from the drive shaft during acceleration
Drive Shaft Noise Characteristics During Acceleration: Identifying Common Causes
Acceleration places significant stress on a vehicle’s drivetrain, including the drive shaft, which transfers power from the transmission to the differential. When abnormal noises occur during this process, they often indicate issues with components like universal joints (U-joints), center support bearings, or alignment. Understanding the specific characteristics of these noises—such as their pitch, frequency, and timing—helps diagnose the root cause effectively. Below is a detailed breakdown of how drive shaft-related noises manifest during acceleration and what they signify.
High-Pitched Whining or Humming Under Load
A persistent high-pitched whining or humming noise that intensifies as the vehicle accelerates is a common symptom of drive shaft-related problems. This sound typically originates from worn or improperly lubricated U-joints or CV joints. U-joints rely on needle bearings to rotate smoothly, and a lack of grease—due to a ruptured seal or aging lubricant—causes metal-to-metal contact, generating friction and a distinctive whine. Similarly, CV joints in front-wheel-drive or all-wheel-drive vehicles may produce a humming noise if their protective boots are torn, allowing grease to leak and contaminants to enter, accelerating wear.
The noise often becomes more pronounced during acceleration because the drivetrain is under increased torque, forcing the compromised joints to work harder. In some cases, the humming may also indicate a misaligned drive shaft, which causes uneven load distribution and vibrations that resonate as a whine. To differentiate between joint and alignment issues, note whether the noise changes with steering input or remains constant under acceleration. A hum that persists regardless of steering angle is more likely tied to joint wear, while alignment problems may produce noises that fluctuate with drivetrain angles.
Rhythmic Clunking or Thudding During Throttle Input
A rhythmic clunking or thudding noise that coincides with engine RPM or throttle changes during acceleration often points to loose or damaged U-joints. These joints connect the drive shaft to the transmission and differential, allowing flexibility as the suspension moves. If the U-joint bearings wear out or the retaining clips loosen, the joint develops excessive play, causing it to shift position abruptly under load. This movement creates a clunking sound that repeats with each rotation of the drive shaft, especially noticeable during rapid acceleration or deceleration.
In two-piece drive shaft systems, a worn center support bearing can produce similar noises. This bearing holds the intermediate section of the drive shaft in place, and if it fails, the shaft may sag or vibrate excessively, striking surrounding components during acceleration. The clunking may also be accompanied by vibrations felt through the floorboard or steering wheel, indicating severe wear. Inspecting U-joints for visible play by hand (with the vehicle safely lifted) and checking the center support bearing for damage or looseness helps confirm the source of the noise.
Grinding or Growling Noises at Higher Speeds During Acceleration
A grinding or growling noise that emerges as the vehicle accelerates to higher speeds—typically above 30–40 mph—often suggests severe wear or misalignment in the drive shaft assembly. This type of noise is commonly associated with damaged or bent drive shafts, which may rub against chassis components or experience internal stress due to imbalance. A bent shaft creates uneven rotation, forcing bearings and joints to work harder, leading to friction-induced grinding. Additionally, a misaligned drive shaft can cause the differential or transmission to operate at abnormal angles, generating growling noises as gears or bearings wear prematurely.
Another potential cause is a failing center support bearing in a two-piece drive shaft. If the bearing’s rubber mount deteriorates, the shaft may shift laterally during acceleration, creating contact with the transmission tunnel or other nearby parts. This contact produces a grinding sound that worsens with speed. To diagnose this issue, inspect the drive shaft for signs of physical damage, such as dents or scratches, and check the center support bearing for excessive movement or wear.
Drive shaft-related noises during acceleration often stem from worn U-joints, CV joints, or alignment issues. High-pitched whining indicates joint friction, while clunking noises suggest loose components like U-joints or center support bearings. Grinding or growling sounds point to severe wear, misalignment, or physical damage to the drive shaft. Addressing these noises promptly through visual inspection, lubrication checks, and component replacement prevents further drivetrain damage and ensures safe operation. Regular maintenance, including joint inspections and alignment verifications, helps minimize acceleration-related drive shaft issues.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
