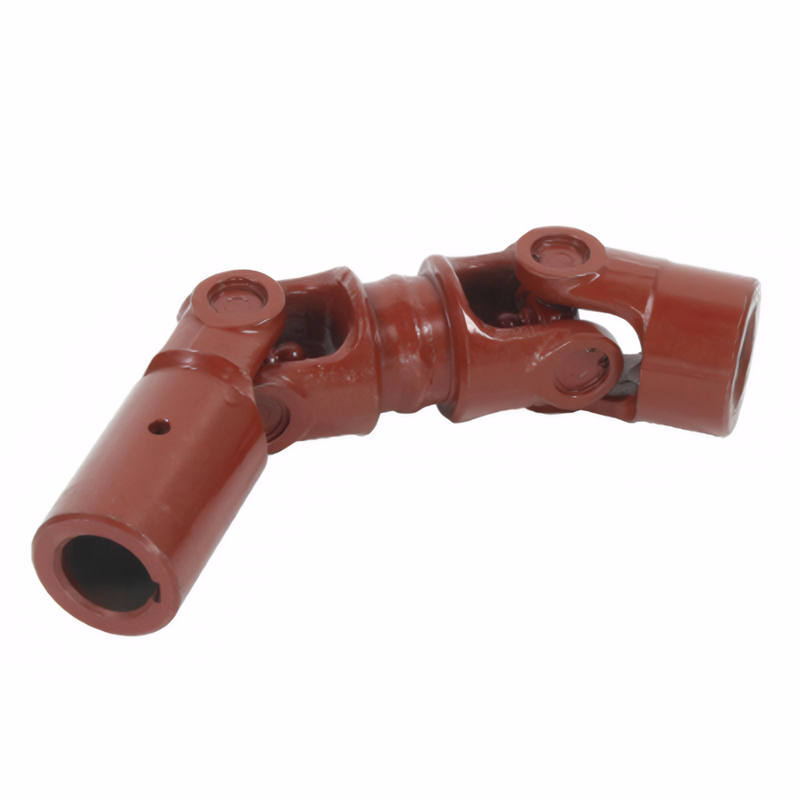
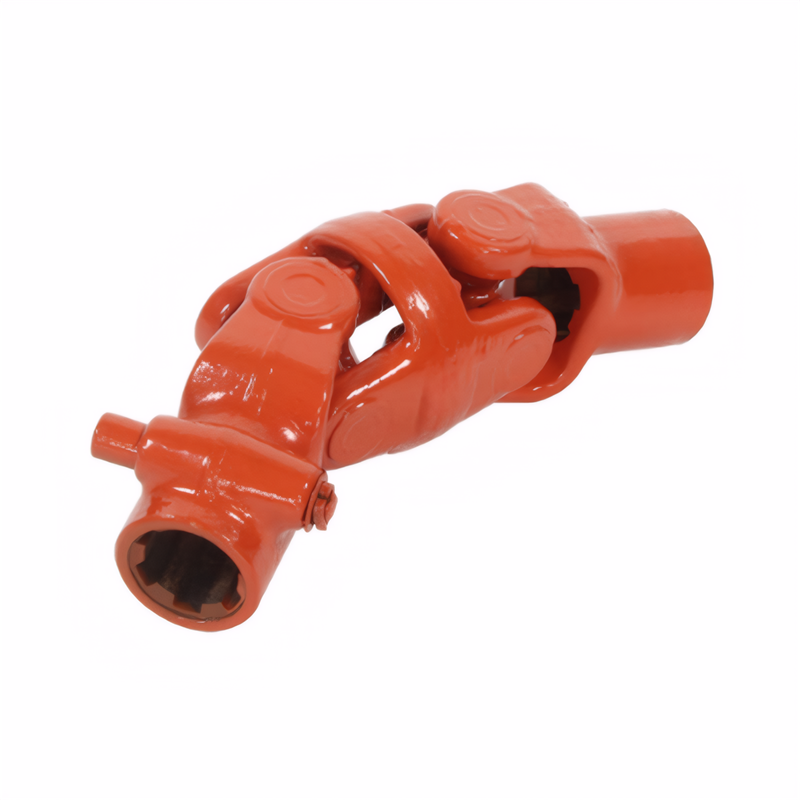
Selection of shock-absorbing materials for drive shafts
Key Considerations for Selecting Vibration-Damping Materials in Drive Shafts
Drive shafts are critical components in automotive and industrial systems, requiring materials that balance mechanical strength, vibration absorption, and environmental resistance. The choice of damping materials directly impacts system longevity, noise reduction, and operational efficiency. Understanding the interaction between material properties and application requirements is essential for engineers and designers.
Material Performance Under Dynamic Loads
Drive shafts operate under continuous rotational forces, generating vibrations that can lead to premature wear or failure. Damping materials must absorb kinetic energy while maintaining structural integrity. Metals like alloy steels (e.g., 40Cr, 30CrMnTi) are commonly used for shaft cores due to their high tensile strength and fatigue resistance. These materials undergo heat treatments such as quenching and tempering to enhance surface hardness and core ductility, ensuring they withstand dynamic stresses without cracking.
For applications involving high-speed rotation or variable loads, composite materials combining metals with viscoelastic polymers are increasingly adopted. These hybrids leverage the stiffness of metals and the energy-dissipating properties of polymers to reduce resonance frequencies. Studies show that such composites can lower vibration amplitudes by up to 40% compared to traditional steel shafts, extending component lifespans in heavy-duty machinery.
Thermal Stability and Environmental Resistance
Drive shafts often operate in extreme temperatures, from sub-zero climates to engine compartments exceeding 120°C. Damping materials must resist thermal degradation while maintaining consistent performance. Silicon-based adhesives and elastomers, for example, exhibit excellent thermal stability, retaining elasticity from -60°C to 230°C. This makes them suitable for automotive drive shafts exposed to fluctuating ambient conditions.
Chemical resistance is equally critical. Materials in contact with lubricants, fuels, or road salts must avoid swelling or corrosion. Fluoropolymer coatings, known for their inertness, are applied to metal surfaces to prevent chemical attack. In marine or industrial settings, stainless steel alloys with chromium content above 12% are preferred for their resistance to oxidation and pitting, ensuring reliable damping over decades of use.
Vibration Isolation and Noise Reduction
Effective vibration isolation requires materials that decouple mechanical energy from the system. Rubber-metal isolators, combining natural rubber’s damping capacity with steel’s rigidity, are widely used in automotive drive shafts. These isolators reduce noise levels by 5–10 decibels by absorbing high-frequency vibrations generated during gear shifts or uneven terrain navigation.
Advanced solutions include magnetorheological fluids, which alter viscosity under magnetic fields to adapt damping forces in real time. This technology, though costly, is employed in precision machinery where variable loads demand dynamic response. For cost-sensitive applications, layered damping systems using constrained viscoelastic layers (e.g., asphalt-based composites) provide effective noise reduction at lower frequencies, typical in off-road vehicles.
Fatigue Resistance and Longevity
Drive shafts endure millions of stress cycles, making fatigue resistance a priority. Materials like tempered martensitic steels (e.g., 42CrMo4) are selected for their ability to resist crack propagation under cyclic loading. Surface treatments such as nitriding or shot peening further enhance fatigue life by introducing compressive residual stresses that counteract tensile forces during operation.
In contrast, cast iron components, while cost-effective, are prone to fatigue in high-stress applications. However, advancements in ductile iron grades with graphite nodules improve toughness, making them viable for lighter-duty drive shafts. Engineers must weigh initial costs against long-term maintenance requirements when selecting materials for fatigue-prone environments.
Integration with Manufacturing Processes
Material selection must align with manufacturing capabilities. Machinability, weldability, and formability influence production efficiency. For instance, low-carbon steels (e.g., S235JR) are easier to machine than high-alloy grades, reducing tool wear and processing time. Additive manufacturing techniques, such as selective laser melting, enable the production of complex geometries in titanium or nickel alloys, which are traditionally difficult to machine but offer superior strength-to-weight ratios.
Thermal expansion coefficients also play a role in assembly tolerance. Materials with mismatched expansion rates can induce stresses during temperature fluctuations, leading to premature failure. Designers often use finite element analysis (FEA) to simulate thermal behavior and optimize material pairings, ensuring compatibility across drive shaft components.
By evaluating dynamic load performance, thermal and chemical resistance, vibration isolation capabilities, fatigue endurance, and manufacturing feasibility, engineers can select damping materials that enhance drive shaft reliability and efficiency. Each property must be tailored to the specific operating conditions, whether in passenger vehicles, industrial machinery, or aerospace systems.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
