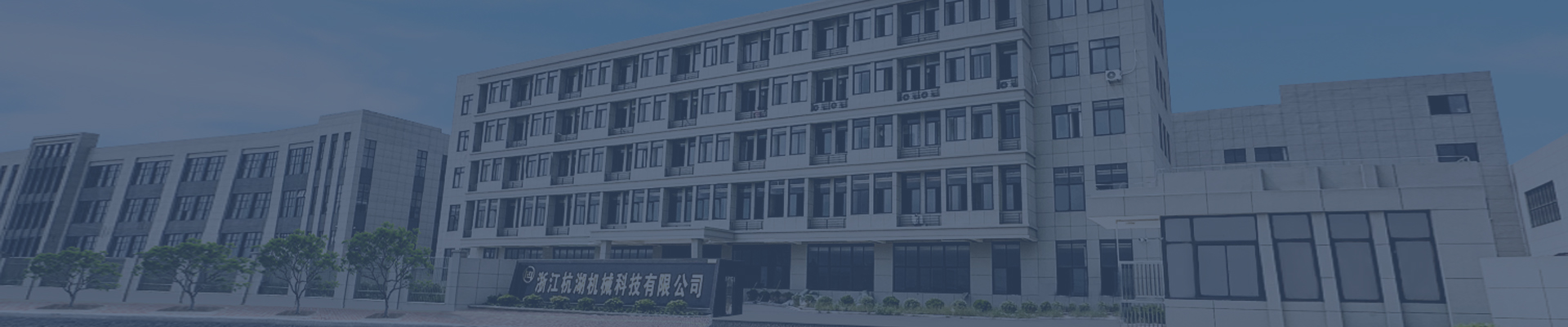
The maximum torque parameter of the drive shaft
Understanding Maximum Torque in Drive Shafts
Maximum torque in a drive shaft represents the peak rotational force it can transmit without failure. This parameter is critical for ensuring the drive shaft can handle the stresses imposed by the engine, transmission, and driving conditions. Engineers calculate maximum torque based on factors such as material strength, shaft geometry, and intended application to prevent premature wear or catastrophic failure.
The relationship between torque and rotational speed is inverse. At lower speeds, the drive shaft can transmit higher torque, while at higher speeds, torque capacity decreases. This dynamic is crucial in applications like electric vehicles, where drive shafts must balance high torque during acceleration with efficient high-speed operation. Advanced materials and design optimizations, such as hollow shafts or composite layers, help manage this trade-off by reducing weight while maintaining strength.
Factors Influencing Maximum Torque Capacity
Material properties play a pivotal role in determining a drive shaft’s maximum torque. High-strength steels, such as 42CrMo4, are commonly used due to their excellent fatigue resistance and ability to withstand cyclic loading. Alloying elements like chromium and molybdenum enhance hardenability, allowing the shaft to maintain structural integrity under repeated stress.
Geometric design also affects torque capacity. Hollow drive shafts reduce weight without significantly compromising strength, as the material is concentrated near the outer surface where stress is highest. The diameter and wall thickness of the shaft are optimized to balance torque transmission and rotational inertia. Additionally, the inclusion of splines or flanges at connection points ensures secure power transfer while accommodating misalignment.
Thermal and environmental factors further influence torque performance. High operating temperatures can reduce material strength, leading to potential failure. Drive shafts in extreme conditions, such as off-road vehicles or industrial machinery, often incorporate heat-resistant coatings or alloys. Corrosion resistance is equally vital, as exposure to moisture, chemicals, or road salts can degrade materials over time, reducing torque capacity and lifespan.
Design Considerations for Enhanced Torque Performance
Dynamic load analysis is essential for predicting how a drive shaft will perform under real-world conditions. Finite element analysis (FEA) simulations help engineers identify stress concentrations and optimize the shaft’s geometry to distribute loads evenly. This process ensures the drive shaft can handle peak torque demands during acceleration, braking, or sudden load changes without exceeding material limits.
Vibration damping is another critical consideration. Excessive vibrations can lead to fatigue failure, reducing the drive shaft’s effective torque capacity. Materials with inherent damping properties, such as viscoelastic polymers, are sometimes integrated into the design to absorb vibrations. Additionally, precision balancing during manufacturing minimizes imbalance, which can induce harmful stresses and reduce torque transmission efficiency.
Manufacturing tolerances directly impact torque performance. Tight control over dimensions, such as diameter and straightness, ensures consistent power transmission. Advanced machining techniques, like CNC turning and grinding, achieve the necessary precision. Surface treatments, such as nitriding or shot peening, enhance fatigue resistance by introducing compressive residual stresses, which counteract tensile forces during operation. These processes collectively improve the drive shaft’s ability to handle maximum torque over its service life.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
