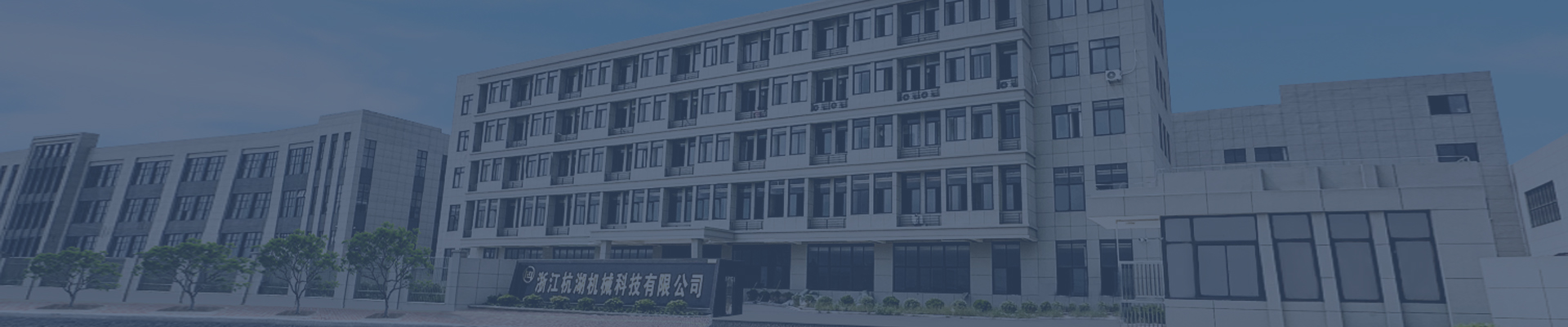
Noise level standards for drive shafts
Transmission Shaft Noise Level Standards: Technical Insights and Industry Benchmarks
Transmission shafts are critical components in automotive drivetrains, responsible for transferring torque from the engine to the wheels. However, excessive noise generated by these components can degrade vehicle comfort, indicate mechanical faults, and even compromise safety. This article explores the technical standards governing transmission shaft noise levels, their underlying causes, and mitigation strategies.
Low-Frequency Noise (5 Hz–50 Hz): Structural and Torsional Resonances
Low-frequency noise, typically ranging from 5 Hz to 50 Hz, is often linked to structural flexing or torsional oscillations in the transmission shaft. These frequencies align with rotational speeds of many engines and drivetrains, making them a common source of concern. For example, a straight-six engine operating at 3,000 rpm generates a fundamental firing frequency of 50 Hz (3,000 ÷ 60), which can excite torsional modes in the shaft if resonance conditions are met.
Symptoms of low-frequency noise include steering wheel wobble, floorboard vibrations, and audible clunking during gear shifts. These issues are particularly pronounced in heavy-duty vehicles or those with long drivetrains, where the shaft’s natural bending frequency may overlap with operational speeds. Misaligned universal joints or worn couplings can exacerbate these vibrations, leading to premature fatigue in shaft components.
Diagnostic techniques for low-frequency issues include torsional vibration analyzers, which measure angular displacement at the shaft ends. A 10 Hz torsional oscillation, for instance, might indicate a loose flange or imbalanced mass distribution. Addressing these problems often involves rebalancing the shaft, adjusting joint angles, or reinforcing structural supports.
Mid-Frequency Noise (50 Hz–500 Hz): Gear Mesh and Bearing Interactions
Mid-frequency noise, spanning 50 Hz to 500 Hz, is frequently associated with gear mesh dynamics and bearing defects. A typical automotive transmission shaft rotating at 4,000 rpm generates a fundamental rotational frequency of 66.7 Hz (4,000 ÷ 60), with harmonics extending into the mid-frequency range due to gear tooth interactions. For example, a 10-tooth pinion meshing with a 30-tooth gear at 66.7 Hz creates a 200 Hz excitation (66.7 Hz × 3 harmonics).
Bearing-related noise in this range often stems from defects like pitting or misalignment. A roller bearing with a localized defect might produce a 150 Hz vibration, corresponding to the number of rolling elements passing the fault site per revolution. These vibrations can propagate through the shaft, causing noise in the cabin or accelerating wear in adjacent components.
Frequency analysis tools, such as FFT spectrum analyzers, are critical for identifying mid-frequency issues. A peak at 300 Hz during acceleration, for instance, could indicate a gear tooth fracture or a damaged bearing cage. Mitigation strategies include improving gear tooth profiles, using higher-precision bearings, or optimizing lubrication to dampen vibrations.
High-Frequency Noise (500 Hz–4,000 Hz): Aerodynamic and Microstructural Effects
High-frequency noise, from 500 Hz to 4,000 Hz, is less perceptible to occupants but critical for component longevity. These frequencies often arise from aerodynamic forces, such as wind turbulence around exposed shafts, or microstructural resonances in composite materials. For example, a carbon-fiber transmission shaft might exhibit a natural frequency of 1,200 Hz due to its stiffness-to-weight ratio, which could resonate with high-speed rotational harmonics.
At these frequencies, vibrations can induce micro-cracks in metal shafts or delamination in composites. A study on a commercial vehicle driveline found that vibration amplitudes exceeding 0.3 mm at 2,000 Hz reduced bearing life by 30%. High-frequency excitations also propagate through connected components, such as differential gears or half-shafts, amplifying noise in the cabin.
Advanced diagnostics for high-frequency issues include laser vibrometry and accelerometer arrays. A 3,500 Hz vibration detected near a shaft flange, for instance, might indicate a loose bolt or cracked weld, requiring immediate inspection. Damping materials, such as viscoelastic coatings, are often applied to shafts to absorb high-frequency energy and prevent resonance.
Critical Factors Influencing Noise Levels
Several design and operational parameters affect the noise levels of transmission shafts:
- Material Selection: Composite shafts have higher natural frequencies than steel due to their lower density and higher stiffness. A carbon-fiber shaft’s first bending mode might occur at 1,500 Hz, compared to 800 Hz for a steel equivalent.
- Geometric Tolerances: A 0.2 mm radial runout in a flange can shift vibration frequencies by 10–15 Hz, altering resonance conditions.
- Operating Speed: Critical speeds occur when rotational frequency matches natural frequencies. For a shaft with a 1,200 Hz natural frequency, operating above 72,000 rpm (1,200 Hz × 60) risks resonance.
- Load Variations: Sudden torque spikes, such as those during gear shifts, can excite higher-order modes. A 50 N·m torque impulse might induce a 1,000 Hz vibration in a lightweight shaft.
By analyzing these factors, engineers can optimize shaft designs to avoid resonance, reduce noise, and extend service life.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
