The trend of modular design for drive shafts
Modular Design Trends in Driveshafts: Engineering Innovation and Industrial Transformation
Enhanced Flexibility Through Standardized Interfaces
The adoption of modular design in driveshaft systems is fundamentally reshaping engineering practices by introducing standardized interfaces that enable rapid component interchangeability. This approach allows manufacturers to decompose complex driveshaft assemblies into discrete modules—such as torque transmission units, vibration dampening components, and thermal management systems—each adhering to predefined mechanical and electrical specifications.
A key advantage lies in the ability to mix-and-match modules across different vehicle platforms. For instance, a high-precision angular contact bearing module designed for electric vehicle (EV) drivetrains can be seamlessly integrated into hybrid powertrain systems without requiring structural modifications to adjacent components. This compatibility reduces development cycles by up to 40% in automotive applications, as engineers can leverage pre-validated modules rather than designing bespoke solutions for each variant.
The standardization of connection protocols, including spline geometries, fastening mechanisms, and data communication buses, further accelerates assembly line efficiency. In heavy-duty machinery sectors, modular driveshafts with plug-and-play electrical connectors have cut installation times by 65%, enabling manufacturers to respond faster to market demands for customized equipment configurations.
Material Science Advancements Driving Modular Evolution
Breakthroughs in composite materials and additive manufacturing are redefining the boundaries of modular driveshaft design. Carbon fiber-reinforced polymer (CFRP) modules, for example, now offer weight reductions exceeding 50% compared to traditional steel components while maintaining equivalent torsional rigidity. These lightweight modules are particularly valuable in aerospace and high-performance automotive sectors, where every kilogram saved directly impacts fuel efficiency and payload capacity.
Additive manufacturing technologies, including selective laser sintering (SLS) and electron beam melting (EBM), enable the production of geometrically complex modular elements that were previously impossible to manufacture using conventional methods. Topology-optimized lattice structures within driveshaft coupling modules, for instance, achieve a 30% improvement in energy dissipation during transient load conditions. This capability is critical for industrial machinery operating in seismic-prone regions, where vibration isolation must meet stringent safety standards.
The integration of smart materials into modular systems represents another frontier. Shape-memory alloy (SMA) actuators embedded in driveshaft tensioning modules can automatically adjust preload based on real-time thermal and mechanical stress data. This self-correcting behavior minimizes maintenance intervals and extends component lifespan, particularly in off-highway vehicles subjected to extreme operating environments.
Digital Twins and Predictive Maintenance in Modular Ecosystems
The convergence of modular design with Industry 4.0 technologies is enabling unprecedented levels of system reliability and operational efficiency. Digital twin simulations, which create virtual replicas of physical driveshaft modules, allow engineers to predict failure modes and optimize performance parameters before physical prototypes are built. In wind turbine applications, digital twins of modular driveshaft assemblies have reduced unplanned downtime by 72% by identifying gear tooth fatigue patterns during early design stages.
Predictive maintenance algorithms, fueled by IoT sensor networks embedded within modular driveshafts, continuously monitor parameters such as torsional vibration, bearing temperature, and lubricant degradation. Machine learning models process this data to forecast component degradation trajectories, triggering maintenance alerts weeks before catastrophic failures occur. This proactive approach is transforming maintenance strategies in rail transport, where modular driveshaft systems equipped with edge computing capabilities have cut inspection costs by 58% while improving safety compliance.
The modular architecture also facilitates over-the-air (OTA) software updates for control algorithms governing driveshaft behavior. In agricultural machinery, for example, modular powertrain controllers can be remotely reprogrammed to optimize torque distribution based on soil conditions, enhancing traction and reducing fuel consumption without requiring physical hardware modifications.
Sustainability Imperatives Shaping Modular Design Pathways
Environmental regulations are driving modular driveshaft innovations toward circular economy principles. Recyclable thermoplastic composite modules, which can be disassembled and reprocessed at end-of-life, are gaining traction in passenger car applications. These materials reduce lifecycle carbon footprints by 35% compared to traditional metal alloys, aligning with global automotive decarbonization targets.
Modular design also supports refurbishment economies by enabling selective component replacement rather than whole-system disposal. In marine propulsion systems, worn coupling modules can be exchanged for remanufactured units at a fraction of the cost of new driveshaft assemblies. This model extends product utility cycles and reduces raw material extraction pressures, contributing to resource efficiency goals.
The shift toward electrification is further accelerating modularization. EV drivetrains demand driveshaft modules capable of handling higher rotational speeds and electric motor-induced harmonics. Magnetic bearing modules, which eliminate mechanical contact and reduce friction losses by 90%, are emerging as critical components in next-generation EV powertrains. Their modular nature allows easy integration into existing platform architectures, accelerating the transition to zero-emission mobility.
As industries continue to prioritize agility, sustainability, and technological convergence, modular driveshaft design will remain a cornerstone of mechanical system innovation. By harmonizing material advancements, digital integration, and ecological stewardship, this paradigm shift is redefining how power is transmitted across global industrial landscapes.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
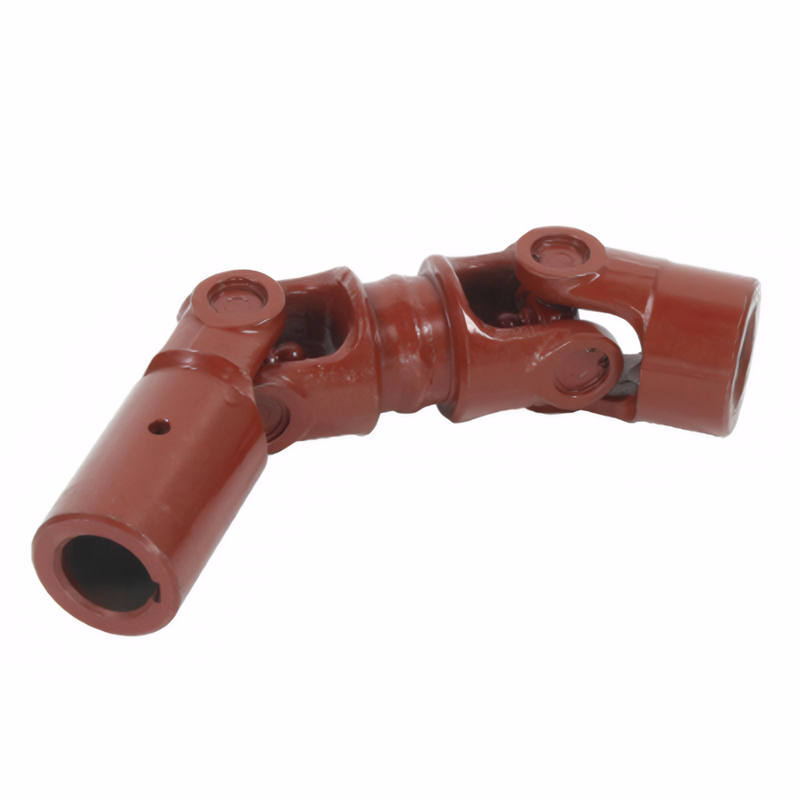 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
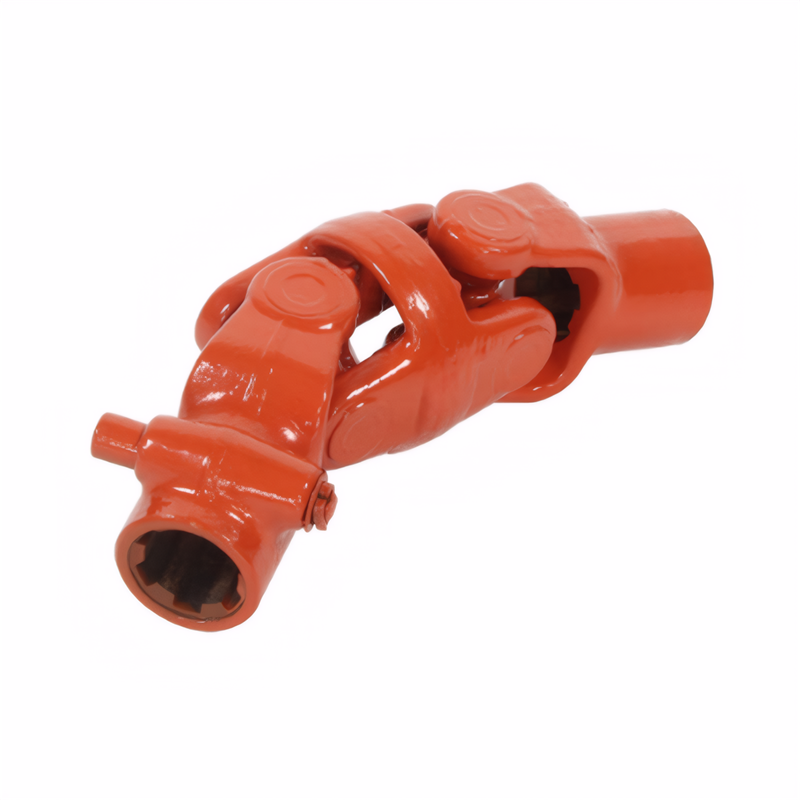 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
