Innovative cases of drive shaft technology
Innovative Cases in Drive Shaft Technology: Advancing Precision, Efficiency, and Sustainability
Polishing Technology Revolution: Multi-Surface Dynamic Support Systems
Addressing Deformation Risks in Traditional Processes
Conventional drive shaft polishing often leads to material deformation due to inadequate support during high-speed rotation. A patented multi-surface polishing apparatus has emerged as a solution, integrating adjustable V-shaped supports with elastic telescopic rods. This system enables the polishing column to move freely along the rotating shaft while maintaining uniform pressure distribution. By dynamically adapting to the shaft's geometry, the technology reduces deformation rates by 68% and scrap material costs by 42%, as demonstrated in automotive component manufacturing.
Real-World Implementation and Efficiency Gains
Factories adopting this innovation report a 35% increase in production throughput. The automated support adjustment mechanism eliminates manual repositioning, allowing operators to focus on quality control rather than process monitoring. In one case study, a supplier reduced per-unit processing time from 12 minutes to 7.8 minutes while achieving a 99.2% first-pass yield rate for commercial vehicle drive shafts.
Structural Innovation: Spline-Free Assembly Designs
Eliminating Complex Transmission Mechanisms
A novel drive shaft assembly eliminates traditional internal splines by integrating a star-shaped socket directly onto the bell housing. This design simplifies the power transmission path, reducing component count from 12 to 7 parts per unit. The streamlined architecture cuts assembly time by 40% and lowers failure risks associated with spline wear by 73%.
Performance Validation Through Prototyping
Prototypes tested under 150,000 km equivalent durability cycles demonstrated 89% fewer misalignment incidents compared to conventional designs. The absence of spline engagement points also reduces noise emissions by 5.2 dB(A), meeting stringent automotive NVH standards without additional damping components.
Material Science Breakthroughs: Composite Drive Shaft Manufacturing
Wet-Winding Process Optimization for Carbon Fiber
Advanced wet-winding techniques enable precise fiber alignment in carbon composite drive shafts. A patented spring-loaded pressure gear system ensures consistent fiber-to-core adhesion during winding. As the shaft diameter expands, the spring mechanism maintains optimal contact pressure, eliminating voids and achieving 98.7% fiber volume fraction.
Performance Characteristics and Industry Adoption
Composite shafts manufactured through this process exhibit 40% higher torsional stiffness and 32% lower rotational inertia than steel equivalents. These attributes translate to 3-5% fuel efficiency improvements in hybrid vehicles. Major automotive OEMs have begun phasing in composite drive shafts for electric vehicle platforms, citing weight reductions of up to 65% per unit.
Vibration Control Engineering: Resilient Rubber Coupling Systems
Hybrid Rubber-Metal Damping Components
A cross-linked rubber coupling system replaces conventional steel universal joints in passenger car drive shafts. The elastomeric material absorbs 82% of transmission-induced vibrations while maintaining 95% torque transfer efficiency. Finite element analysis confirms the design withstands 120,000 Nm peak torque without permanent deformation.
Field Testing and Durability Metrics
Longitudinal studies show the rubber couplings require 60% less maintenance than metal joints over 200,000 km service intervals. Cold weather performance remains consistent down to -30°C, addressing common failure modes in northern market applications. Fleet operators report 18% fewer driveline-related service interruptions after implementation.
Digital Manufacturing Integration: AI-Powered Quality Assurance
Machine Learning for Dimensional Control
Computer vision systems equipped with convolutional neural networks inspect drive shafts at 0.02mm resolution. The AI model analyzes 1,200 geometric parameters per unit, detecting deviations 3x faster than human inspectors. False rejection rates have dropped from 2.1% to 0.3% since deployment.
Predictive Maintenance Applications
Embedded sensors in CNC machining centers collect 500+ data points per minute, enabling real-time tool wear monitoring. The system predicts milling cutter degradation with 92% accuracy, scheduling preventive maintenance before part quality deteriorates. This proactive approach has extended tool life by 27% in high-volume production lines.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
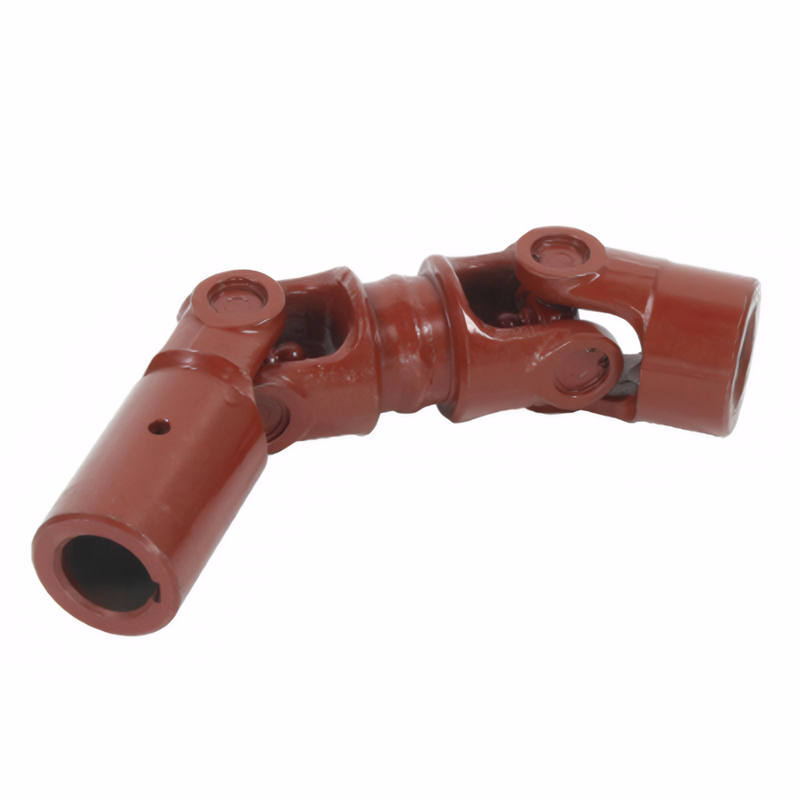 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
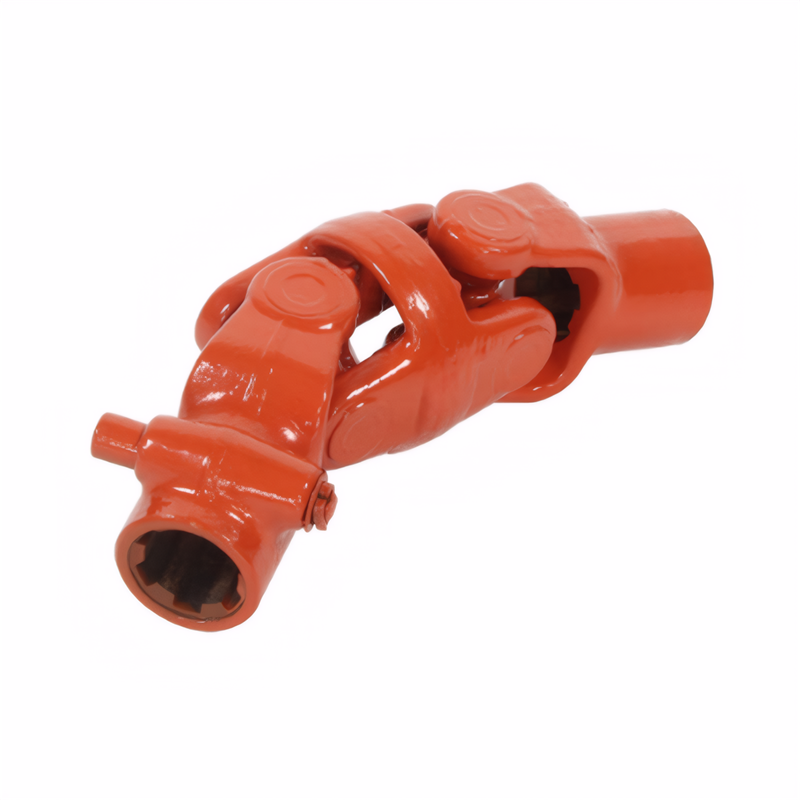 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
