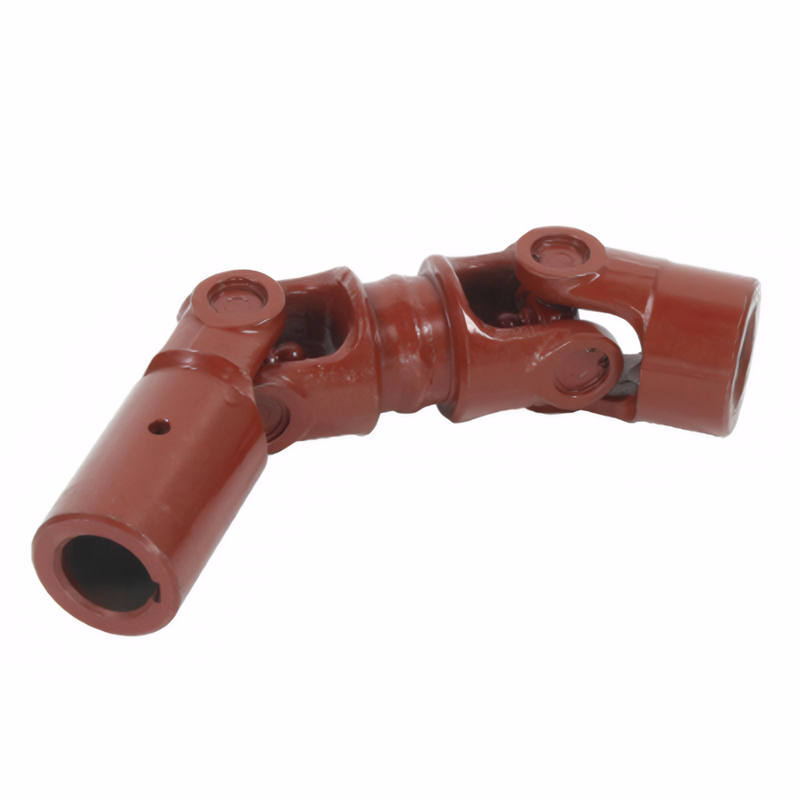
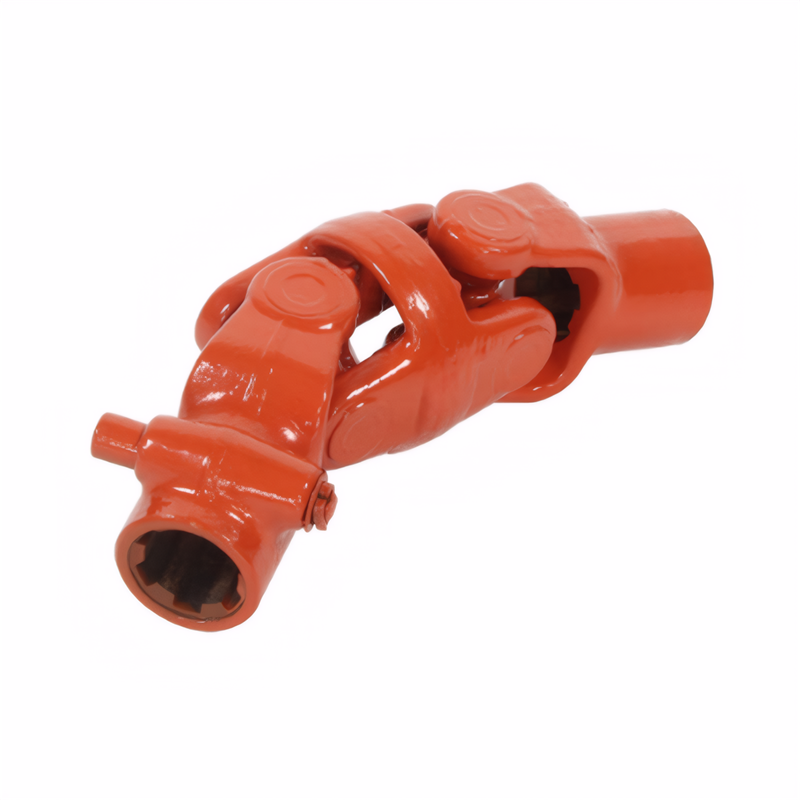
Universal joint drive shaft Angle adjustment and adaptation techniques
Universal Joint Drive Shaft Angle Adjustment: Practical Techniques for Precision Fit
Understanding Angle Impact on Transmission Stability
The angle between universal joints and drive shafts directly affects power transmission efficiency. When two universal joints form a double-jointed configuration, the difference in their working angles should remain below 0.5° to eliminate output speed fluctuations. For example, measuring a rear universal joint at 19.5° and rotating the shaft 90° to measure 17° yields a 2.5° angle difference, which exceeds the recommended threshold. This misalignment causes vibration during acceleration and deceleration, particularly noticeable in rear-wheel-drive vehicles when shifting between forward and reverse gears.
To maintain optimal angles, adjust the rear universal joint by inserting wedge-shaped metal pads between the leaf spring and rear axle mount. For front universal joints, modify the transmission rear support through pad thickness adjustments or replacement. A damaged transmission mount, often caused by ATF leakage from the oil pan seal, can distort angles and should be replaced immediately.
Angle Measurement and Correction Methods
Precision Measurement Techniques
Use an inclinometer placed on the universal joint bearing cap, ensuring proper leveling before recording angles. Rotate the drive shaft 90° for a second measurement and calculate the angle difference. This process reveals hidden misalignments that cause uneven tire wear and steering pull.
Structural Adjustment Strategies
When dealing with excessive angles:
- Rear Axle Modification: Inserting wedge pads between the leaf spring and axle changes the vertical position of the drive shaft, altering the working angle.
- Transmission Support Adjustment: Adding or removing shims under the transmission rear mount corrects front universal joint angles.
- Component Replacement: Worn universal joints with visible play require immediate replacement to prevent angle degradation.
For vehicles with long wheelbases, consider intermediate shafts to equalize drive shaft angles on both sides. This prevents steering pull caused by unequal torque distribution during acceleration.
Dynamic Balance and Vibration Control
Critical Speed Considerations
Drive shafts behave as flexible shafts, with critical speeds determined by diameter, length, and support conditions. Never exceed 80% of the calculated critical speed (n_max = 0.8n_c). For high-speed applications, reduce shaft length, add intermediate supports, or upgrade to larger diameter tubes.
Angle-Induced Vibration Solutions
When angle differences exceed 0.5°:
- Double-Jointed Systems: Ensure both universal joints operate in the same plane with angles below 12° each (18-20° combined).
- Constant Velocity Joints: Ball cage-type CV joints maintain equal angular velocity up to 40° misalignment, ideal for front-wheel-drive applications.
- Flexible Couplings: Rubber-damped joints absorb minor misalignments but require regular inspection for elastic degradation.
During maintenance, check for metal clunking noises caused by flower key interference. Clean and lubricate all splines with high-temperature grease, removing burrs with a metal file before reassembly.
Advanced Angle Management for Specialized Applications
Off-Road Vehicle Considerations
Four-wheel-drive systems demand precise angle matching between front and rear drive shafts. Use angle gauges to verify that both shafts maintain identical working angles during suspension articulation. Installing adjustable-length drive shafts with sliding yokes compensates for suspension travel while maintaining angle integrity.
High-Performance Vehicle Tuning
For racing applications, implement telescoping drive shafts with built-in angle sensors. These systems continuously monitor and adjust angles during high-speed cornering, preventing power loss from excessive misalignment. Pair with lightweight aluminum drive shafts to reduce rotational inertia while maintaining critical speed margins.
Commercial Vehicle Optimization
Heavy-duty trucks require angle calculations considering starting torque (M_p = i_g × M_emax) and adhesion torque (M_Φ). Select drive shafts with yield torque (M_s) exceeding calculated scale torque (M_GW) to prevent permanent deformation. For articulated vehicles, use angle-compensating universal joints at hinge points to maintain power transmission during steering maneuvers.
Maintenance Protocols for Long-Term Reliability
Lubrication Best Practices
Apply synthetic chassis grease to all splines and universal joint bearings every 30,000 miles. Use needle-type grease fittings for precise lubrication delivery, avoiding over-pressurization that could damage seals.
Inspection Checklist
- Visual inspection for cracks in bearing caps
- Measurement of end play in universal joints
- Verification of bolt torque specifications
- Check for grease leakage around seals
Failure Prevention Measures
Replace universal joints exhibiting rust pitting or abnormal wear patterns immediately. Store spare drive shafts horizontally to prevent bending, and avoid impact damage during handling. When reinstalling, ensure proper alignment marks match to prevent phase errors in double-jointed systems.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
