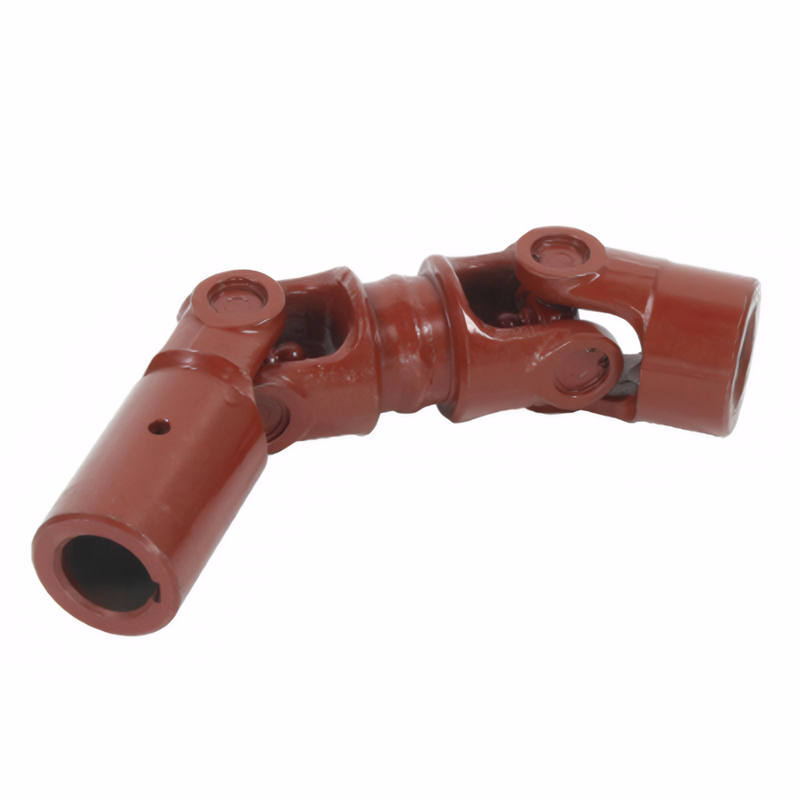
Key points for low-noise design of electric vehicle drive shafts
Low-Noise Design Essentials for Electric Vehicle Driveshafts
The absence of an internal combustion engine in electric vehicles (EVs) shifts noise perception dynamics, making transmission system vibrations and sounds more pronounced. Driveshaft design must prioritize noise reduction through material selection, structural optimization, and precision engineering to meet evolving consumer expectations for silent mobility.
Material Innovation for Vibration Damping
Traditional metal bearings in driveshafts generate significant friction and noise under high-speed rotation. Advanced polymers like polyetheretherketone (PEEK) offer a breakthrough solution. PEEK bearings exhibit an elastic modulus of 3.8 GPa—lower than steel but higher than standard plastics—enabling controlled deformation to absorb vibrations. Their damping coefficient is 5–10 times greater than metal, reducing vibration transmission by 60% in real-world applications.
For example, replacing steel bearings with PEEK variants in a metro train’s转向架 (bogie) system lowered vibration acceleration from 0.5g to 0.2g, cutting cabin noise from 75–80 dB to 65–70 dB. In EVs, PEEK bearings in motor shafts reduce dynamic friction coefficients to 0.15–0.2 (vs. 0.3–0.4 for steel), cutting energy loss by 40% and motor noise from 72 dB to 58 dB. Lightweight PEEK components (1/5 the density of steel) also reduce rotational inertia, enhancing system responsiveness.
Precision Engineering for Angular Alignment
Driveshaft misalignment due to suspension travel or component wear introduces uneven load distribution, exacerbating noise. Cardan joint (universal joint) angles must be strictly controlled to minimize inertial torque fluctuations.
- Single Cardan Joints: Best suited for angles below 3° to balance cost and performance. Designs should ensure phase alignment between joints to cancel secondary vibrations.
- Double Cardan Joints: Required for angles exceeding 3° to split the operating angle into smaller segments, reducing harmonic vibrations.
- Constant Velocity (CV) Joints: Ideal for steep angles (e.g., front-wheel-drive EVs), maintaining consistent velocity to eliminate speed fluctuations.
Angular acceleration should remain below 300 rad/s² to prevent fatigue failure. In one EV model, restricting Cardan joint angles to ≤2.5° reduced driveshaft-induced vibrations by 35% during acceleration.
Dynamic Balancing and Resonance Avoidance
Imbalanced driveshafts generate centrifugal forces proportional to rotational speed squared, causing high-frequency noise. Dynamic balancing involves:
- High-Precision Machining: Tolerances for shaft runout and concentricity must be ≤0.05 mm to prevent imbalance.
- Counterweight Adjustment: Adding or removing material at strategic points to neutralize mass discrepancies.
- Resonance Damping: Using viscoelastic coatings or tuned mass dampers to absorb vibrations at critical frequencies (e.g., 2,000–5,000 Hz, where human ear sensitivity peaks).
In a high-speed EV test, applying a 0.5 mm-thick damping layer to the driveshaft reduced peak noise levels by 12 dB at 120 km/h.
Gear and Bearing Optimization for Smooth Power Transmission
Gear meshing noise dominates EV transmission sounds. Solutions include:
- High-Precision Gear Cutting: Maintaining backlash within 0.05–0.15 mm and profile deviations below 0.02 mm to minimize impact forces.
- Helical Gear Adoption: Spiral-tooth designs distribute load gradually, reducing noise by 8–10 dB compared to spur gears.
- Bearing Preload Adjustment: Optimal preload (typically 5–15 N for EVs) eliminates play without inducing excessive friction.
A study on EV differential gears showed that increasing contact ratio from 1.6 to 2.2 reduced gear whine by 7 dB.
Thermal and Environmental Adaptability
EV driveshafts operate in extreme conditions, from -40°C in winter to 60°C under heavy load. PEEK bearings maintain stable friction coefficients across this range, avoiding lubricant degradation-induced noise spikes. In cold climates, self-lubricating PEEK variants eliminate grease thickening issues, reducing startup noise by 25%.
Implementation Insights
- Simulation-Driven Design: Use finite element analysis (FEA) to predict vibration modes and optimize component stiffness.
- Modular Testing: Validate noise performance at subsystem (e.g., gearbox) and full-vehicle levels.
- Supplier Collaboration: Work with bearing manufacturers to customize PEEK composites with 10% elastic particles for enhanced damping.
By integrating these strategies, EV makers can achieve driveshaft noise levels below 50 dB at highway speeds, aligning with consumer demand for “library-grade” cabin silence. As 5G and IoT technologies mature, embedded sensors in driveshafts will enable real-time vibration monitoring, further refining noise control through predictive maintenance.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
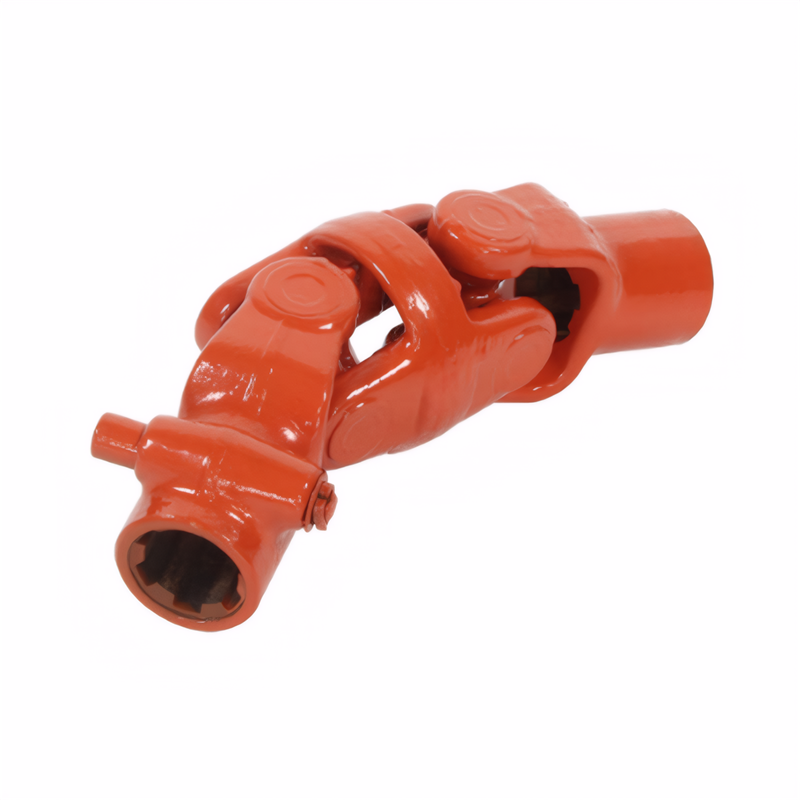
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
