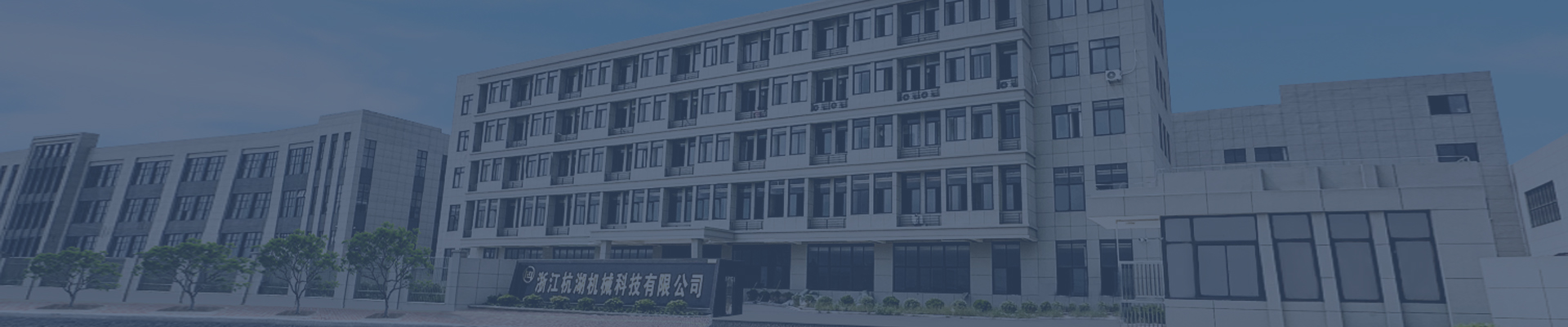
Selection of the connection method for the drive shaft
Selection Criteria for Transmission Shaft Connection Methods
Key Factors Influencing Connection Method Selection
The choice of transmission shaft connection method depends on multiple engineering parameters, including load characteristics, operational environment, and spatial constraints. For instance, automotive applications prioritize vibration isolation and angular misalignment compensation, while industrial machinery emphasizes torque transmission efficiency and maintenance accessibility.
In agricultural equipment, such as tractor power take-off (PTO) systems, cross-axis connections using universal joints are common. These joints accommodate angular deviations up to 45 degrees, enabling flexible power transmission between the engine and implements. Conversely, high-precision CNC machine tools typically employ rigid flange couplings to minimize torsional backlash, ensuring sub-micron positional accuracy during milling operations.
Environmental factors also play a critical role. Chemical processing plants often utilize magnetic couplings to eliminate physical contact between shafts, preventing corrosion from aggressive media. This non-contact design also reduces maintenance frequency by avoiding seal wear, a common failure point in traditional mechanical connections.
Common Connection Methods and Their Applications
Rigid Coupling Systems
Rigid couplings, including sleeve and flange types, provide direct torque transfer with minimal energy loss. These connections require precise alignment during installation, as misalignment exceeding 0.1mm can induce premature bearing failure. A case study in wind turbine gearboxes demonstrated that rigid couplings reduced power transmission losses by 3% compared to flexible alternatives, but demanded quarterly laser alignment checks to maintain performance.
In conveyor systems, rigid couplings excel at transmitting high torque across short distances. A mining operation reported a 15% increase in conveyor uptime after switching from chain drives to rigid shaft couplings, attributing the improvement to reduced chain elongation and sprocket wear. However, this method requires rigid mounting frames to prevent vibration amplification.
Flexible Coupling Solutions
Elastic couplings incorporating polyurethane or rubber elements address misalignment issues in variable-speed applications. A packaging machinery manufacturer reduced motor vibration by 40% by replacing rigid couplings with elastic variants, extending gearbox service life from 18 to 36 months. These couplings typically tolerate angular misalignment up to 2 degrees and axial displacement of ±1mm.
For applications requiring larger angular ranges, double-jointed universal couplings offer flexibility up to 30 degrees. Automotive drivetrains frequently employ this design to accommodate suspension movement while maintaining power continuity. A durability test on commercial vehicle propeller shafts showed that double-universal joints with needle bearing inserts withstood 1 million load cycles without failure, outperforming single-joint designs by 300%.
Non-Contact Transmission Technologies
Magnetic couplings eliminate mechanical wear by transmitting torque through magnetic fields. This design proves advantageous in sterile environments like food processing, where lubricant contamination must be avoided. A dairy plant reported a 50% reduction in cleaning validation time after adopting magnetic couplings for agitator drives, as the hermetic seal prevented product ingress into bearing housings.
However, magnetic couplings have torque limitations, typically maxing out at 500Nm for standard designs. Advanced eddy-current couplings overcome this by inducing electromagnetic fields in conductive rotors, enabling torque transmission up to 5,000Nm. These systems find applications in large-scale pumps and compressors, where soft-start capabilities reduce electrical stress during motor initialization.
Application-Specific Selection Guidelines
High-Precision Manufacturing
CNC machining centers demand connection methods that minimize torsional compliance. Rigid flange couplings with precision-ground mating surfaces reduce positional error to ±0.005mm, critical for five-axis milling operations. A aerospace component manufacturer achieved IT6 surface finishes on titanium parts after upgrading to zero-backlash couplings, eliminating chatter marks caused by flexible drive elements.
Heavy-Duty Industrial Equipment
Mining conveyors and crushing systems require connections capable of withstanding shock loads up to 5 times the rated torque. Gear couplings with hardened alloy steel sleeves demonstrate superior durability in these conditions, surviving impact events without tooth fracture. A copper mine reported a 200% increase in coupling lifespan after switching from elastomer-based designs to gear couplings, attributing the improvement to better load distribution across multiple teeth.
Mobile Machinery Applications
Agricultural tractors and construction equipment face constant misalignment due to uneven terrain. Constant-velocity joints (CVJs) maintain constant rotational speed despite angular deviations, preventing power fluctuations during PTO operation. A field test showed CVJs reduced implement vibration by 60% compared to standard universal joints when operating on sloped fields, improving operator comfort and tool longevity.
For marine propulsion systems, flexible rubber couplings dampen engine vibrations before they reach the hull structure. A ferry operator measured a 12dB reduction in cabin noise levels after installing vibration-isolating couplings, enhancing passenger comfort without compromising thrust efficiency. These couplings typically feature multiple rubber layers to target specific frequency ranges for optimal noise attenuation.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
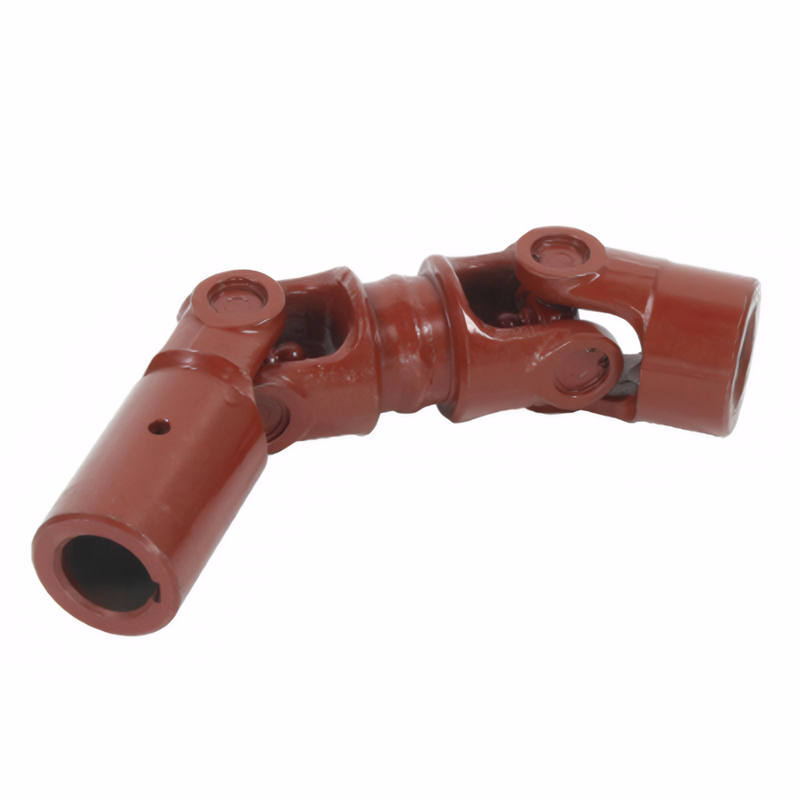 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
