Wear detection of universal joints for drive shafts
Comprehensive Guide to Detecting Wear in Drive Shaft Universal Joints
Drive shaft universal joints are critical components in automotive powertrain systems, facilitating torque transmission while accommodating angular misalignment between shafts. Their wear and failure can lead to vibration, noise, and even catastrophic mechanical breakdowns. This guide outlines practical methods to detect universal joint wear, enabling timely maintenance and preventing costly repairs.
Visual Inspection Techniques
Exterior Component Analysis
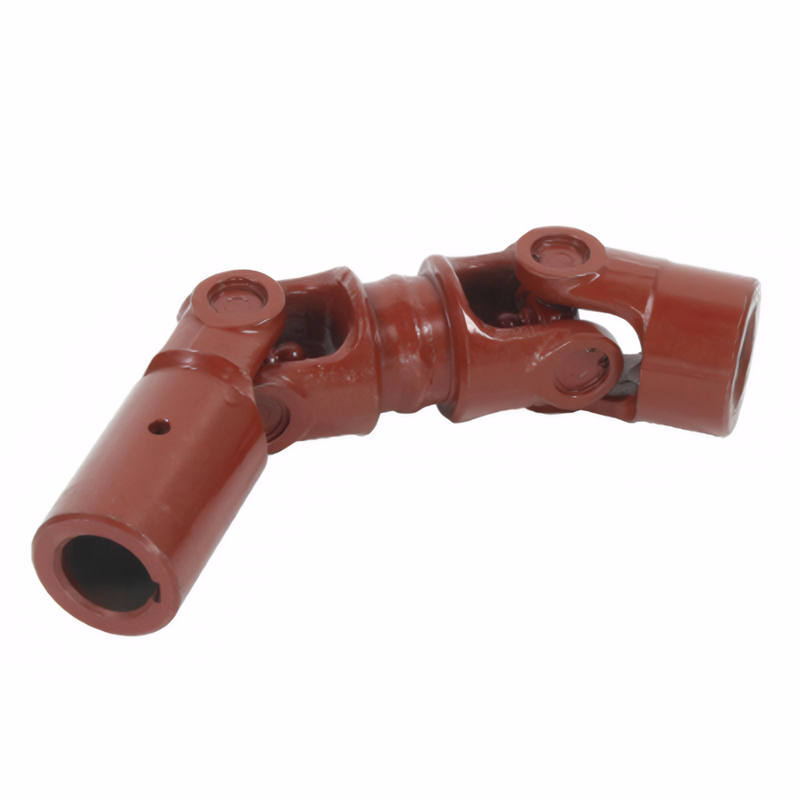
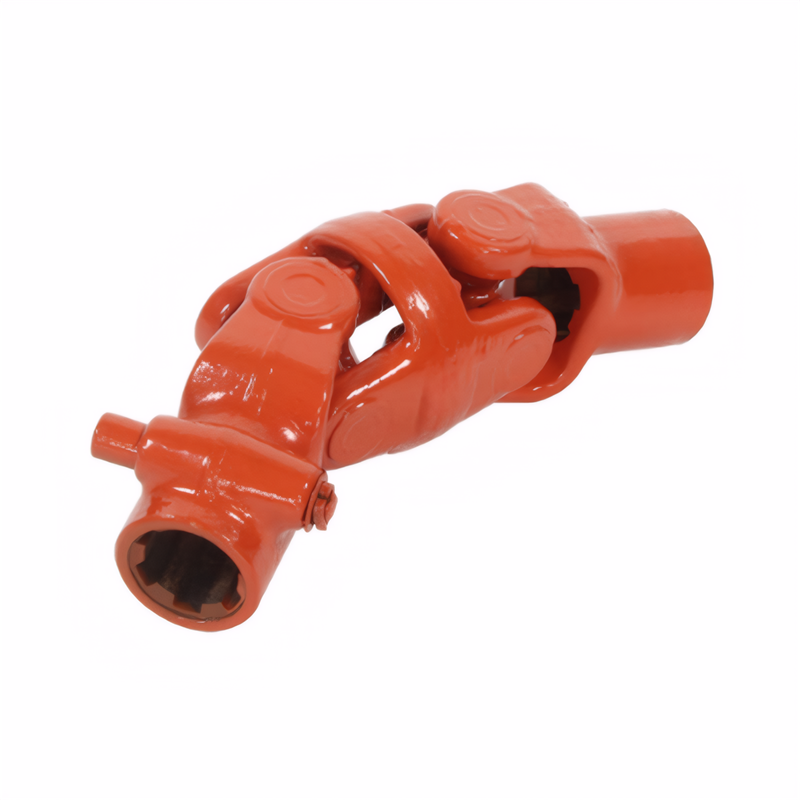
Begin by examining the universal joint's outer components for visible damage. Look for cracks or deformation on the cross-axis housing, which often result from excessive loads or impact damage. These structural compromises disrupt the joint's ability to rotate smoothly.
Next, inspect the protective rubber boots covering the joint. Cracked or torn boots allow dirt, water, and debris to infiltrate the internal components, accelerating wear. A grease-stained boot may indicate internal leakage, signaling potential lubrication failure.
Internal Wear Indicators
For a more detailed assessment, manually rotate the joint while observing its movement. Excessive play or grinding noises suggest worn needle bearings or a damaged cross-axis. In severe cases, the joint may lock up or produce a clunking sound during rotation, indicating critical failure.
Operational Symptom Monitoring
Noise and Vibration Analysis
During vehicle operation, pay attention to unusual sounds emanating from the transmission or driveline. A rhythmic clunking during acceleration or deceleration often points to a worn universal joint, particularly if the noise intensifies when turning. High-frequency squealing or whining may indicate insufficient lubrication or bearing damage.
Vibration is another telltale sign. A universal joint with excessive wear can cause the drive shaft to wobble, transmitting vibrations through the chassis. These vibrations typically worsen at higher speeds and may be accompanied by steering wheel shake or seat vibrations.
Power Transmission Efficiency
A degraded universal joint can reduce power transmission efficiency, manifesting as sluggish acceleration or uneven torque delivery. If the vehicle struggles to maintain speed on inclines or exhibits hesitation during gear changes, the universal joint may be the culprit.
Advanced Diagnostic Methods
Physical Measurement and Disassembly
For a precise assessment, disassemble the universal joint and measure key components. Use calipers to check the cross-axis diameter against manufacturer specifications. Wear beyond acceptable limits necessitates replacement.
Examine the needle bearings for signs of pitting, scoring, or discoloration, which indicate overheating or contamination. Similarly, inspect the bearing races for wear patterns, as uneven surfaces can cause binding or excessive play.
Dynamic Testing Procedures
Dynamic testing involves evaluating the joint's performance under simulated operating conditions. This can be done using specialized equipment that applies rotational forces while monitoring vibration and noise levels. Elevated readings in these parameters suggest internal wear or misalignment.
Another dynamic test involves lifting the vehicle and rotating the wheels while observing the drive shaft's behavior. A universal joint with excessive wear will cause the shaft to exhibit noticeable runout or irregular rotation, indicating the need for replacement.
Proactive Maintenance Strategies
Lubrication Management
Regular lubrication is essential for extending universal joint lifespan. Follow the manufacturer's recommended service intervals and use high-quality grease compatible with the joint's materials. Over-lubrication can cause seal failure, while under-lubrication leads to premature wear.
Environmental Protection
Protect universal joints from environmental contaminants by ensuring protective boots remain intact. Replace damaged boots immediately to prevent debris ingress. Additionally, avoid driving through deep water or mud, as these conditions can introduce moisture and abrasive particles into the joint.
Load and Angle Optimization
Minimize stress on universal joints by avoiding excessive loads or sharp steering angles. Overloading the vehicle or operating it at extreme angles can accelerate wear and reduce component life. Adjust driving habits to maintain optimal operating conditions for the driveline.
By implementing these detection methods and maintenance strategies, vehicle owners and technicians can effectively identify and address universal joint wear before it leads to more severe problems. Regular inspections and proactive care are key to ensuring reliable power transmission and extending the service life of drive shaft components.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
