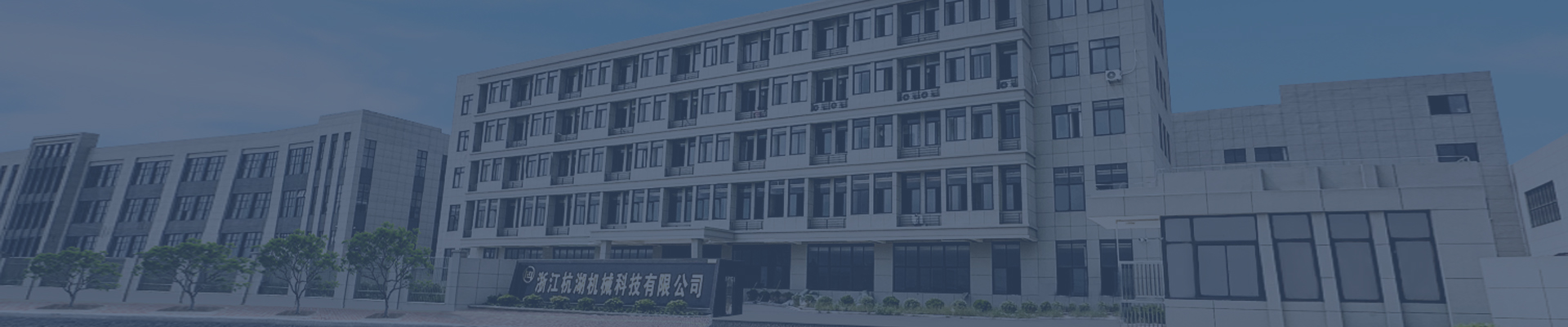
Judgment of damage to the ball cage of the drive shaft
How to Identify Damaged CV Joints in Drive Shafts
CV joints, also known as constant velocity joints, are critical components in a vehicle's drivetrain system. They connect the drive shaft to the wheels, allowing for smooth power transmission even during steering maneuvers. When a CV joint fails, it can lead to various issues that affect vehicle performance and safety. Here’s a detailed guide to identifying damaged CV joints.
Common Symptoms of CV Joint Damage
Unusual Noises During Operation
One of the most noticeable signs of a damaged CV joint is the presence of unusual noises while driving. These noises often manifest as clicking, clunking, or grinding sounds that become more pronounced during specific driving conditions.
- Clicking During Turns: If you hear a rhythmic clicking sound when turning the steering wheel, especially at sharp angles, it could indicate an issue with the outer CV joint. This sound is caused by worn-out bearings or a damaged cage inside the joint, which allows the ball bearings to move irregularly.
- Grinding During Acceleration: A grinding noise that occurs when accelerating, particularly from a stop, may suggest problems with the inner CV joint. This noise is often due to excessive wear or damage to the joint's internal components, causing friction and heat buildup.
- Clunking Over Bumps: If you experience a clunking sound when driving over bumps or uneven road surfaces, it could be a sign of a loose or damaged CV joint. This sound is typically caused by excessive play in the joint, allowing it to move freely and create noise.
Vibration and Shuddering
Damaged CV joints can also cause vibrations and shuddering throughout the vehicle, affecting both comfort and safety.
- Vibration at High Speeds: If you feel a vibration in the steering wheel or through the vehicle's chassis at high speeds, it could be due to a damaged CV joint. This vibration is often caused by an imbalance in the joint's components, leading to uneven power transmission.
- Shuddering During Acceleration: A shuddering sensation when accelerating, particularly from a low speed, may indicate a problem with the CV joint. This shuddering is typically caused by worn-out or damaged internal components that are unable to transmit power smoothly.
Steering and Handling Issues
CV joint damage can significantly impact a vehicle's steering and handling capabilities, making it difficult to control the vehicle effectively.
- Difficulty Steering: If you find it increasingly difficult to turn the steering wheel, especially at low speeds, it could be due to a damaged CV joint. This difficulty is often caused by excessive friction or binding in the joint, preventing it from moving freely.
- Vehicle Pulling to One Side: A vehicle that pulls to one side while driving, even when the steering wheel is held straight, may have a damaged CV joint. This pulling is typically caused by an imbalance in power transmission between the two front wheels, often due to a faulty CV joint on one side.
- Uneven Tire Wear: Damaged CV joints can also lead to uneven tire wear, as they affect the alignment and balance of the wheels. If you notice that one tire is wearing faster than the others, it could be a sign of a CV joint problem.
Visual Inspection Techniques
In addition to listening for unusual noises and feeling for vibrations, a visual inspection can also help identify damaged CV joints.
Checking the CV Joint Boots
CV joints are protected by rubber boots that prevent dirt, debris, and moisture from entering the joint. If these boots are damaged or torn, it can lead to premature wear and failure of the CV joint.
- Inspect for Tears or Cracks: Carefully examine the CV joint boots for any signs of tears or cracks. Even small tears can allow contaminants to enter the joint, leading to damage over time.
- Check for Grease Leakage: If you notice grease leaking from the CV joint boots, it could indicate a problem with the joint itself. Grease leakage is often caused by excessive heat or pressure buildup inside the joint, which can damage the internal components.
Examining the CV Joint for Play
Another visual inspection technique involves checking the CV joint for excessive play or movement.
- Lift the Vehicle: Use a jack to lift the vehicle off the ground, ensuring it is securely supported on jack stands.
- Grasp the Wheel and Wiggle: With the vehicle lifted, grasp the wheel at the top and bottom and wiggle it back and forth. If you feel excessive play or movement in the CV joint, it could indicate damage or wear.
- Rotate the Wheel and Listen: While the vehicle is lifted, rotate the wheel by hand and listen for any unusual noises or grinding sounds. These sounds could indicate problems with the CV joint's internal components.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
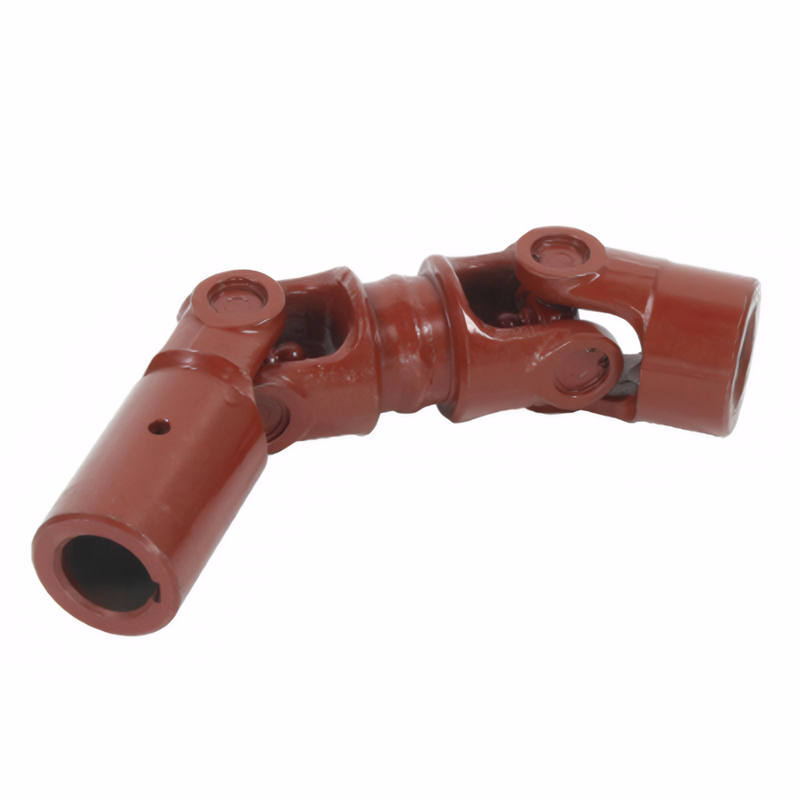 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
