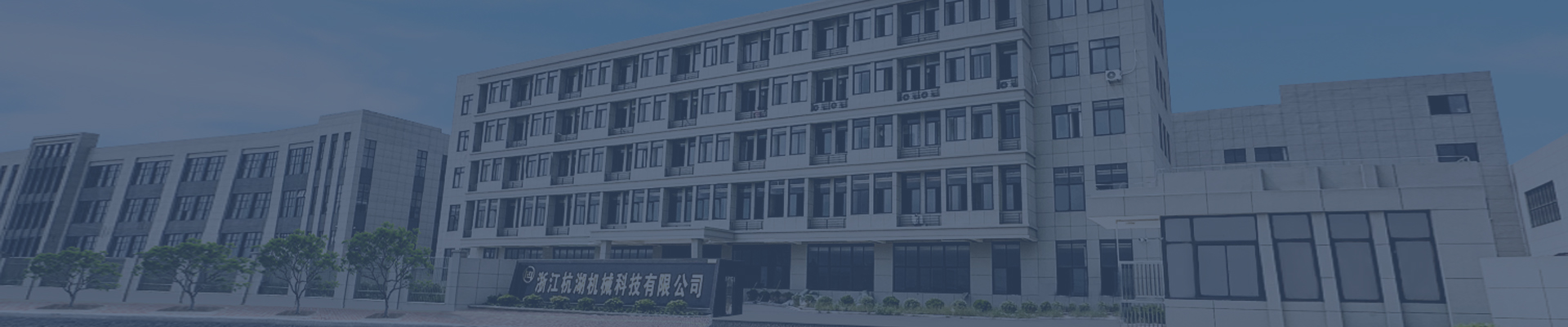
Adjustment of mismatched drive shaft speed
Adjusting Drive Shaft Speed Mismatch Issues
Drive shafts are crucial for transferring rotational power in vehicles and machinery, connecting the power - generating components like engines to the driven parts such as wheels or pumps. When there's a speed mismatch in the drive shaft, it can lead to a range of problems, from inefficient operation to severe mechanical damage. Here's how to tackle this issue.
Understanding the Causes of Drive Shaft Speed Mismatch
To effectively adjust a drive shaft speed mismatch, it's essential to first figure out what's causing it. Several factors can contribute to this problem, and each requires a different approach for resolution.
Gear Ratio Discrepancies
One of the main culprits behind drive shaft speed mismatch is gear ratio discrepancies. In a transmission or gearbox, different gears have specific ratios that determine the speed and torque output. If there's an incorrect gear selection or a problem with the gear - changing mechanism, the drive shaft may not rotate at the expected speed.
For example, in a manual transmission, if the driver accidentally shifts into the wrong gear, the drive shaft speed will be out of sync with the engine speed and the requirements of the driven components. In an automatic transmission, issues like a slipping clutch pack or a malfunctioning valve body can cause incorrect gear engagement, leading to speed mismatch.
Universal Joint Wear or Failure
Universal joints (U - joints) are flexible couplings that allow the drive shaft to transmit power while accommodating angular misalignment between the driving and driven components. Over time, U - joints can wear out due to constant movement, high loads, or lack of lubrication.
When a U - joint wears, it can cause irregular movement of the drive shaft, resulting in speed fluctuations. In severe cases, a completely failed U - joint can cause the drive shaft to bind or even break, leading to a sudden and significant speed mismatch. Signs of U - joint wear include clicking or clunking noises during acceleration or deceleration, as well as visible play in the joint when manually manipulated.
Transmission or Differential Problems
The transmission and differential are key components in the powertrain that work together to distribute power to the wheels and control the drive shaft speed. Any issues within these components can cause speed mismatch.
In the transmission, problems such as low fluid levels, contaminated fluid, or internal mechanical failures can disrupt the normal operation of gears and clutches, affecting the drive shaft speed. The differential, on the other hand, is responsible for allowing the wheels to rotate at different speeds during turns. If the differential has worn gears or a damaged spider gear set, it can cause uneven power distribution and speed variations in the drive shaft connected to the wheels.
Steps to Adjust Drive Shaft Speed Mismatch
Once you've identified the cause of the drive shaft speed mismatch, you can take the appropriate steps to adjust and resolve the issue.
Checking and Correcting Gear Selection
If gear ratio discrepancies are the problem, start by checking the gear selection. In a manual transmission vehicle, ensure that the driver is shifting into the correct gear for the given driving conditions. If the issue persists, inspect the shift linkage for any damage or misalignment that may be preventing proper gear engagement.
For automatic transmissions, use a diagnostic scanner to check for any error codes related to the transmission control module. These codes can provide valuable information about potential problems with gear selection, such as a faulty solenoid or a sensor issue. Based on the diagnostic results, perform the necessary repairs or replacements to restore proper gear selection and drive shaft speed.
Replacing Worn Universal Joints
When U - joint wear is the cause of the speed mismatch, replacing the worn joints is the solution. Start by safely raising the vehicle and supporting it on jack stands. Locate the U - joints on the drive shaft, which are typically located at the ends where the shaft connects to the transmission and the differential.
Use appropriate tools, such as a U - joint press, to remove the old U - joints. Clean the areas around the joints and inspect the drive shaft yokes for any damage. Install new U - joints, making sure they are properly seated and aligned. After installation, lubricate the new U - joints according to the manufacturer's recommendations. Lower the vehicle and test drive it to check if the drive shaft speed mismatch has been resolved.
Servicing the Transmission and Differential
If transmission or differential problems are causing the speed mismatch, a more in - depth service may be required. For the transmission, start by checking the fluid level and condition. If the fluid is low, add the correct type of fluid to the recommended level. If the fluid is contaminated with metal shavings or has a burnt smell, it may indicate internal damage, and a transmission flush or overhaul may be necessary.
For the differential, drain the old fluid and inspect it for metal particles or signs of wear. Replace the differential fluid with the appropriate type and viscosity as specified by the manufacturer. If the differential has worn gears or a damaged spider gear set, it will need to be disassembled, and the damaged components replaced. After servicing the transmission and differential, test drive the vehicle to ensure that the drive shaft speed is now properly matched.
Preventive Measures to Avoid Drive Shaft Speed Mismatch
Taking preventive measures can help avoid drive shaft speed mismatch issues in the future and extend the life of your powertrain components.
Regular Maintenance Checks
Perform regular maintenance checks on your vehicle or machinery, including inspections of the drive shaft, U - joints, transmission, and differential. Look for signs of wear, leaks, or damage during these inspections. Check the fluid levels and conditions in the transmission and differential regularly and change the fluids according to the manufacturer's recommended intervals.
Also, inspect the shift linkage in manual transmissions and the electronic components in automatic transmissions for any signs of wear or malfunction. Early detection of potential problems can prevent them from developing into more serious issues that cause drive shaft speed mismatch.
Proper Lubrication
Proper lubrication is essential for the smooth operation of U - joints, transmissions, and differentials. Ensure that all moving parts are adequately lubricated according to the manufacturer's specifications. Use the correct type of lubricant for each component, as using the wrong type can cause damage and affect performance.
For U - joints, apply grease through the zerk fittings until you see fresh grease oozing out. In transmissions and differentials, use the recommended fluid and change it at the specified intervals to maintain proper lubrication and protect the internal components from wear.
Avoiding Overloading and Rough Driving
Overloading your vehicle or machinery can put excessive stress on the drive shaft and its related components, leading to premature wear and potential speed mismatch issues. Always adhere to the manufacturer's recommended load limits and avoid carrying more weight than the system is designed to handle.
Additionally, rough driving conditions, such as driving over potholes, curbs, or rough terrain at high speeds, can cause damage to the drive shaft, U - joints, and other powertrain components. Drive cautiously in these conditions and avoid sudden impacts that can disrupt the normal operation of the drive shaft and cause speed variations.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
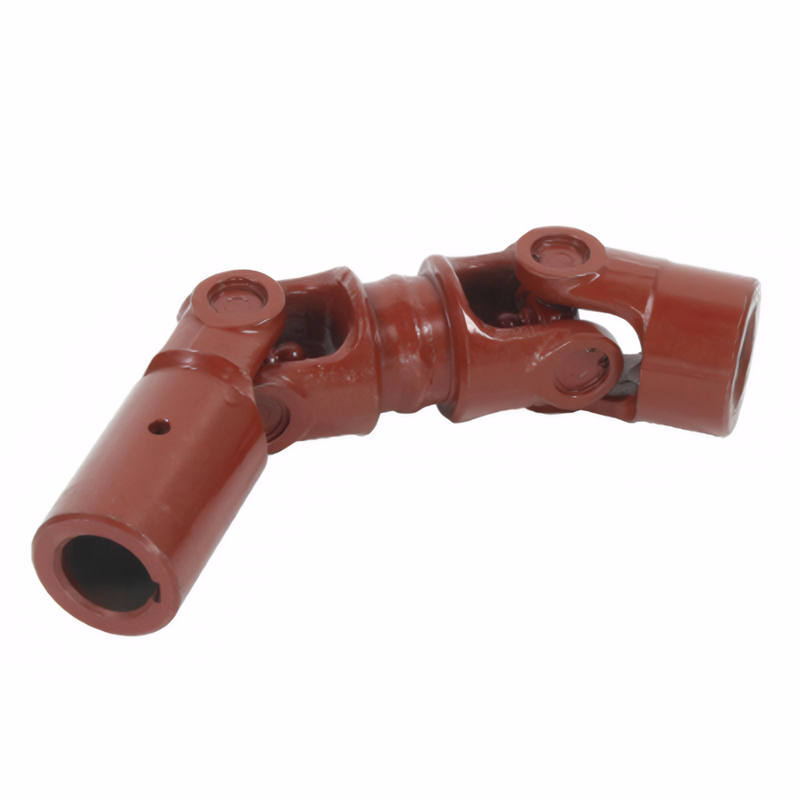 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
