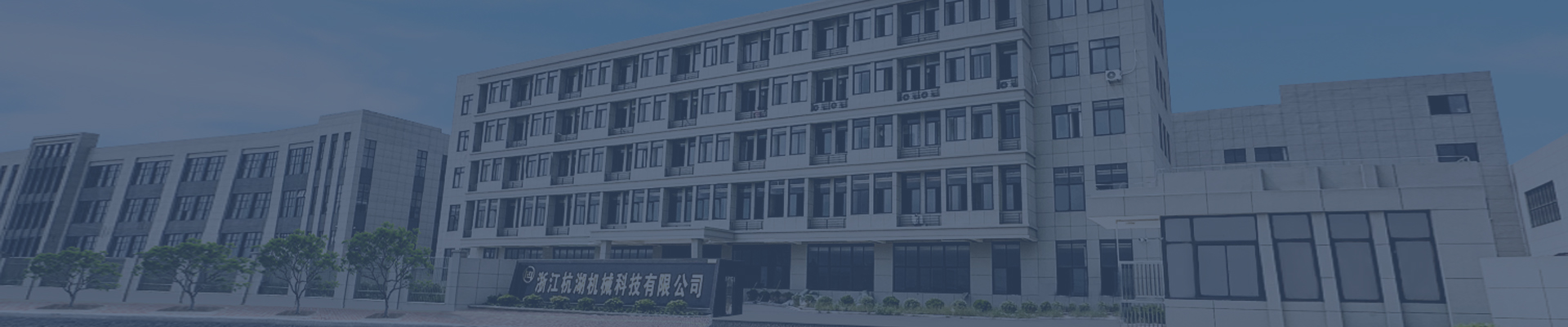
Treatment methods for corrosion spots on drive shafts
Effective Methods for Treating Corrosion Spots on Driveshafts
Driveshafts are critical components in automotive powertrain systems, responsible for transmitting torque from the transmission to the differential. When corrosion spots appear, they compromise structural integrity and operational safety. This guide outlines professional-grade treatment approaches to restore driveshaft performance.
Surface Preparation Techniques
Gentle Rust Removal
Begin by assessing the corrosion severity. For superficial surface rust, use 400-grit sandpaper wrapped around a flexible shaft. Rotate the driveshaft manually while applying uniform pressure to avoid creating uneven surfaces. For deeper pitting, progress to 600-grit sandpaper, focusing on localized areas without widening the affected zones. Always wear nitrile gloves to prevent skin oils from contaminating the metal surface during preparation.
Advanced Cleaning Protocols
After mechanical rust removal, implement a two-stage cleaning process. First, wipe the surface with a lint-free cloth dampened with isopropyl alcohol to eliminate residual particles. Second, perform an ultrasonic cleaning cycle using a 5% citric acid solution heated to 50°C. This dissols microscopic corrosion products while preserving the base metal's structural properties. Rinse thoroughly with deionized water and dry immediately using compressed air directed at a 45-degree angle to prevent water entrapment.
Protective Coating Applications
Wax-Based Barrier Systems
Paraffin wax coatings offer excellent moisture resistance when applied correctly. Melt pharmaceutical-grade paraffin in a double boiler setup, maintaining temperatures between 65-70°C to prevent degradation. Using a natural bristle brush, apply three thin coats with 15-minute intervals between applications. Each layer should achieve 50-70μm thickness, measured with a digital coating thickness gauge. This method creates a semi-permanent barrier that withstands temperatures up to 85°C and prevents electrolyte penetration.
Resin-Enhanced Solutions
For environments with high humidity or salt exposure, consider resin-modified coatings. Prepare a solution by dissolving 200g of rosin in 1L of denatured alcohol, stirring continuously until complete dissolution. Apply using an HVLP spray gun at 2.5 bar pressure, maintaining a 20cm distance from the surface. Three cross-coat applications ensure complete coverage, with each layer flash-off time of 10 minutes at 25°C. This treatment provides superior adhesion and chemical resistance compared to traditional wax methods.
Structural Integrity Restoration
Selective Metal Deposition
When corrosion causes material loss exceeding 15% of cross-sectional area, metal deposition becomes necessary. Using a TIG welding process with ER70S-6 filler rod, build up damaged areas in 0.5mm layers. Maintain interpass temperatures below 150°C to prevent hydrogen embrittlement. After deposition, perform stress relief by heating the entire driveshaft to 250°C for 2 hours, followed by controlled cooling at 10°C per hour. This process restores original dimensions while maintaining mechanical properties.
Dynamic Balancing Verification
Post-repair driveshafts require precision balancing to prevent vibration-induced failures. Mount the component on a hard-bearing balancing machine capable of measuring imbalance down to 0.1g-mm. Perform dual-plane balancing at operating speed, correcting residual imbalance using drill-out or weight addition methods. Ensure final imbalance values remain within OEM specifications, typically ≤5g-mm for passenger vehicles. This step prevents premature wear of universal joints and transmission bearings.
Long-Term Maintenance Strategies
Environmental Control Measures
Implement preventive maintenance by installing driveshaft boots made from neoprene rubber. These protective covers should feature a 360-degree seal to prevent road debris and moisture ingress. For vehicles operating in coastal regions, apply a vapor corrosion inhibitor (VCI) spray quarterly. This creates a molecular protective layer that neutralizes atmospheric contaminants.
Periodic Inspection Protocols
Establish a 12-month inspection cycle using non-destructive testing methods. Employ eddy current testing to detect subsurface corrosion, with sensors calibrated for the specific driveshaft material. Perform visual inspections under UV light to identify coating degradation, looking for fluorescence indicative of barrier breakdown. Document all findings in a vehicle maintenance log to track corrosion progression patterns.
 Method for detecting the stabi
Method for detecting the stabi
 Reliability testing standard f
Reliability testing standard f
 Certification of environmental
Certification of environmental
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
