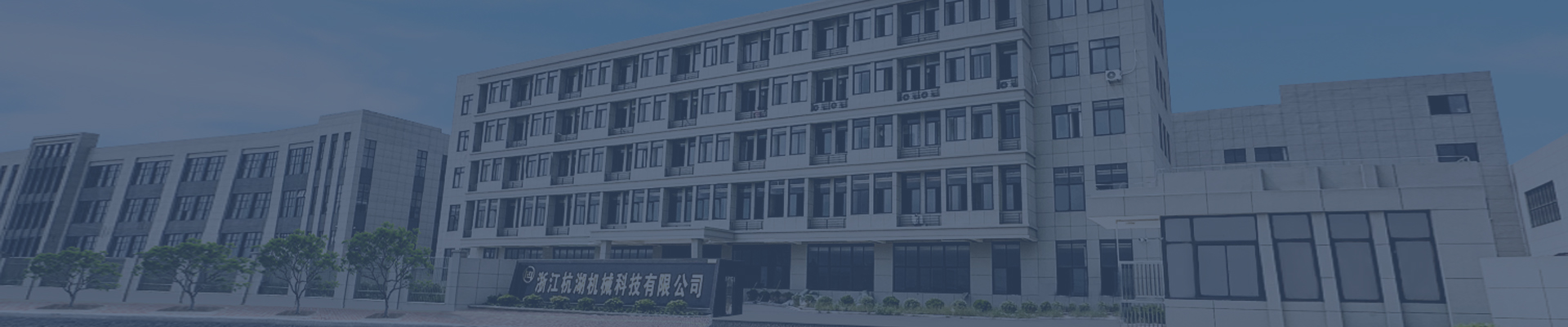
Quality control of forging process for drive shafts
Quality Control in the Forging Process of Drive Shafts
Raw Material Inspection and Selection
The foundation of high-quality drive shaft forging lies in the careful selection and inspection of raw materials. The choice of material depends on the specific application requirements of the drive shaft, such as the load it will bear and the operating environment. Commonly used materials include 45 steel and alloy structural steels.
Before entering the forging process, raw materials must undergo a series of inspections. First, the material's quality certificate from the manufacturer should be verified against the relevant material standards. This ensures that the material meets the specified chemical composition and mechanical property requirements. Next, the material's identification should be checked to prevent mix-ups. The material's specifications, such as diameter and length, should also be confirmed. Additionally, the surface quality of the material should be examined for any defects like cracks, scabs, or excessive roughness. Chemical composition analysis through methods like rapid spectrometers or spark identification can be used to further verify the material's quality.
Heating Process Control
The heating process is a critical step in the forging of drive shafts as it directly affects the material's plasticity and the quality of the forging. Improper heating can lead to issues such as overheating, overburning, or insufficient heating, all of which can compromise the mechanical properties of the drive shaft.
To ensure proper heating, the heating temperature should be strictly controlled. For example, for 45 steel, the forging temperature range is typically from 1200°C to 800°C. The heating process can be monitored using infrared temperature measurement instruments or multi-stage temperature selection devices. These tools help maintain the heating temperature within the desired range. Moreover, the heating time should be carefully calculated based on the material's size and properties. For smaller carbon steel parts with diameters less than 150 - 200 mm, a one-stage heating specification can be used, which includes appropriate heating and holding times to ensure uniform temperature distribution throughout the material.
Forging Process Quality Assurance
The forging process itself requires meticulous control to achieve the desired shape and mechanical properties of the drive shaft. There are different forging methods, such as free forging and die forging, each with its own set of quality control measures.
Free Forging
In free forging, the initial inspection of the first forged piece is crucial. This helps identify any potential issues early in the process. During the forging operation, workers should conduct self-inspections, and inspectors should perform regular checks and record the results. Necessary measuring and gauging tools should be provided to ensure accurate dimensions during forging. For example, when forging a stepped shaft, the length and diameter of each step should be measured frequently to ensure they are within the specified tolerances.
Die Forging
For die forging, the quality control starts with the inspection of the forging dies. The die's quality certificate or manufacturing inspection report, including non-destructive testing results, should be verified. The die should then be inspected for shape, size, and hardness. Before being mounted on the machine, the die should be adjusted, and a sample piece should be forged and inspected for accuracy. If any defects are found during forging, such as insufficient filling of the die cavity or folding, appropriate corrective measures should be taken. For minor insufficient filling, the part can be re-forged in a new die or repaired by welding. However, for important parts, re-forging may not be the best option as it can introduce new defects like oxide skin inclusion.
Post-Forging Heat Treatment and Inspection
After forging, heat treatment is often required to improve the mechanical properties of the drive shaft, such as its hardness, strength, and toughness. The heat treatment process parameters, including heating temperature, holding time, and cooling rate, should be strictly controlled and recorded. For example, during quenching and tempering, the hardness of the drive shaft should be checked at different stages. Workers can perform self-inspections, and inspectors should conduct re-inspections and record the results. In some cases, magnetic hardness sorting instruments or hardness testers can be used for 100% hardness inspection. Additionally, non-destructive testing methods, such as ultrasonic testing or magnetic particle testing, can be employed to check for any internal or surface cracks.
Product Identification and Traceability
To ensure the quality control process is effective, proper product identification and traceability are essential. From the moment the raw materials enter the workshop, they should be labeled with information such as the part number, name, material grade, specification, material heat number, operator, and inspector. These labels should accompany the parts throughout the forging process, including during machining. In some cases, the die serial number and material heat number can be printed directly on the forging. This traceability system allows for quick identification of any quality issues and helps in taking corrective actions promptly. It also facilitates the investigation of the root cause of any defects and the implementation of preventive measures to avoid similar issues in future production batches.
 Transmission shaft safety perf
Transmission shaft safety perf
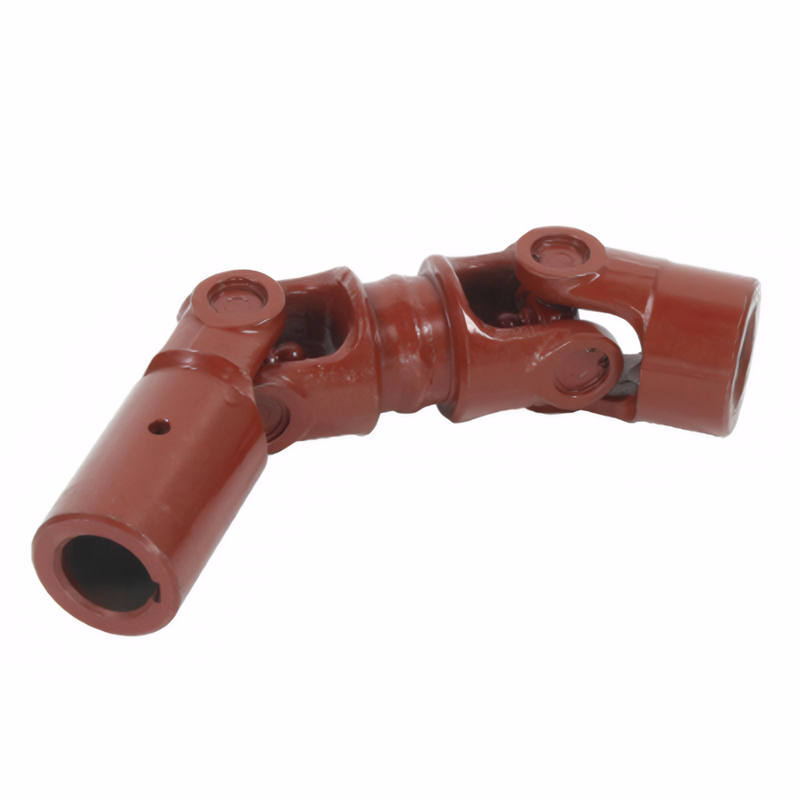 Transmission shaft life test s
Transmission shaft life test s
 Test requirements for transmis
Test requirements for transmis
 Standard for batch inspection
Standard for batch inspection
 简体中文
简体中文 English
English
